This is Intel LGA1155 aka Sandy Bridge (SB) overclocking thread.
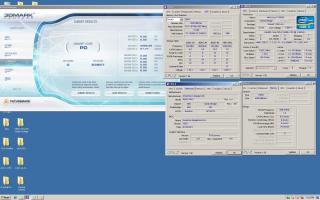
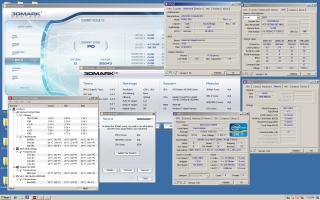
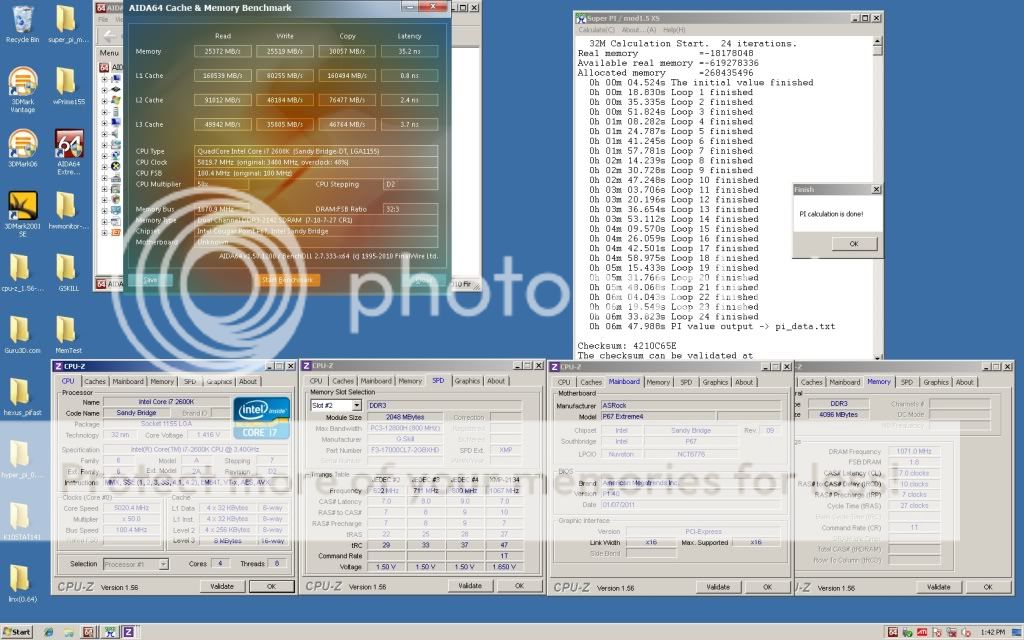
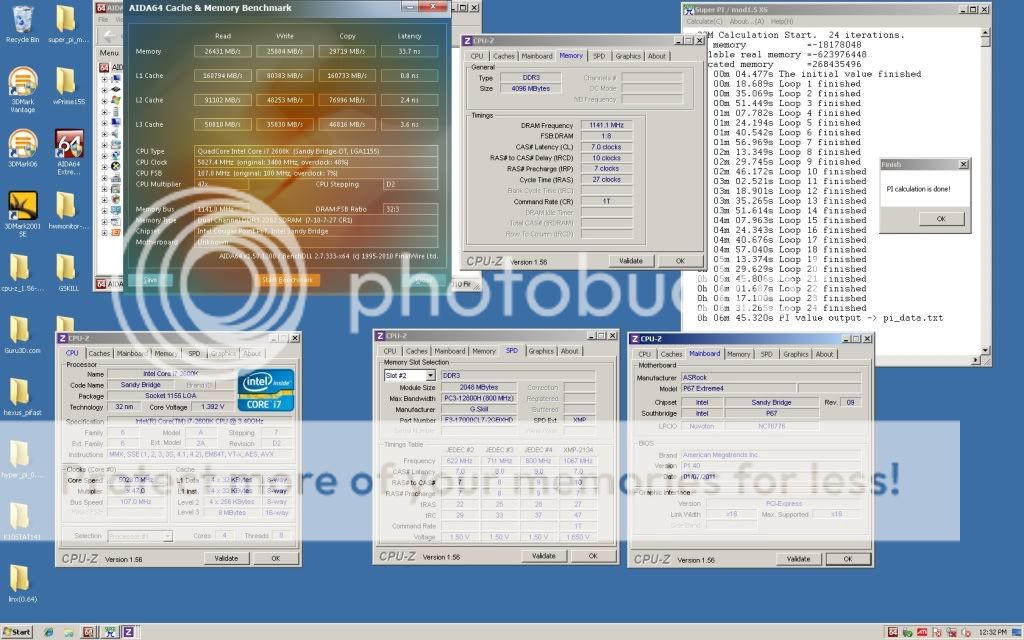
Please share your benchmark, stability, guides etc...

» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «

Latest BIOS:
LINK
BCLK
measured in MHz
Base Clock Increasing your base clock increases your CPU core clocks, memory speed, QPI frequency, and North Bridge Frequency
-Similar to the older FSB “Front Side Bus”
BCLK x CPU ratio = CPU frequency
Adjust the BCLK frequency to overclock the CPU speed!
Multiplier
-Multiplier is a ratio that determines the clock speed for the CPU based on the multiplication of the BCLK. For example, your CPU multiplier determines what your CPU core clock speed is using this formula: Base clock * multiplier
There are also multipliers for Memory frequency, QPI speed, and North Bridge (UCLK) frequency.
PCIE
measured in MHz
Periferal Connect Interface Express
-Video Graphics communication link
when overclocking, increasing the PCI-E clock can help with stability when above 200MHz BCLK
CPU Voltage
AKA -VCore this is your processor core voltage. Increasing this will supply your CPU cores the power they need to operate at higher frequencies.
Central Processing Unit
-Processor core voltage
DO NOT EXCEED 1.55v
IMC Voltage
"VTT" or "QPI" Increasing this will supply the power needed for the IMC (North Bridge) to operate at higher frequencies.
- L3 shared cache
- memory controller
- processor I/O power rail
Since memory controller frequency is dependent on BCLK, the higher the BCLK, the higher the IMC voltage required. DO NOT Exceed 1.45v
DRAM Voltage
DDR3 Random Access Memory
-Memory Voltage
Since DRAM speed is linked to the BCLK the higher the BCLK the higher the DRAM Voltage is needed
CPU PLL Voltage
PLL: Phase Locked Loop voltage
- Processor/IMC(Integrated Memory Controller)/other internal clock cycles
- Clock multiplying of processor is provided by an internal Phase Locked Loop
Does not have a significant effect on CPU Speed, -DO NOT Exceed 1.90v
PCH Voltage
Platform Controller Hub
- main I/O interface for CPU
- display connectivity
- Integrated Audio
- power management features
- Storage features
The higher the CPU frequency, the harder the I/O (input and output) has to work so there is higher power consumption and more heat is generated, raising the CPU temperature. The PCH voltage needs to be increased in order to stabilize I/O signaling. DO NOT EXCEED 1.25v
vroom vroom SB!
OC Guides & Tips:
LGA1155 Overclocking Glossary
Asus P67/Z68 OC Guides
Asus P67 OC Guides
Latest Overclocking Programs, System Info, Benchmarking, & Stability Tools
LINK - credit to stasio
Monitoring Tools:
CPU-Z 1.61
RealTemp 3.70
CoreTemp 1.0 RC3
HWiNFO 3.95
Mem TweakIT 1.01.6
CPU-Tweaker 2.0 Beta 15
Stability/Stressing Tools: - Pls install win7 SP1 for max stressing
LinX 0.6.4 - 10.3.11.019
PS: For those having problems with bench not starting, try to set mem manually or set it a bit lower than "ALL" preset
Intel BurnTest 2.52
Prime95 27.7 Build 2 X64
Prime95 27.7 Build 2 X86
» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
Benchmark Tools:
SuperPI Mod XS 1.5
HyperPI 0.99 Beta
AIDA64 2.30.1900
Cinebench 11.5
wprime 2.09
pifast
maxxmem
AquaMark 3.1
BSOD codes for overclocking
QUOTE
0x101 = increase vcore
0x124 = increase/decrease vcore or QPI/VTT... have to test to see which one it is
0x0A = unstable RAM/IMC, increase QPI first, if that doesn't work increase vcore
0x1E = increase vcore
0x3B = increase vcore
0x3D = increase vcore
0xD1 = QPI/VTT, increase/decrease as necessary, can also be unstable Ram, raise Ram voltage
0x9C = QPI/VTT most likely, but increasing vcore has helped in some instances
0x50 = RAM timings/Frequency or uncore multi unstable, increase RAM voltage or adjust QPI/VTT, or lower uncore if you're higher than 2x
0x109 = Not enough or too Much memory voltage
0x116 = Low IOH (NB) voltage, GPU issue (most common when running multi-GPU/overclocking GPU)
0x7E = Corrupted OS file, possibly from overclocking. Run sfc /scannow and chkdsk /r
0x124 = increase/decrease vcore or QPI/VTT... have to test to see which one it is
0x0A = unstable RAM/IMC, increase QPI first, if that doesn't work increase vcore
0x1E = increase vcore
0x3B = increase vcore
0x3D = increase vcore
0xD1 = QPI/VTT, increase/decrease as necessary, can also be unstable Ram, raise Ram voltage
0x9C = QPI/VTT most likely, but increasing vcore has helped in some instances
0x50 = RAM timings/Frequency or uncore multi unstable, increase RAM voltage or adjust QPI/VTT, or lower uncore if you're higher than 2x
0x109 = Not enough or too Much memory voltage
0x116 = Low IOH (NB) voltage, GPU issue (most common when running multi-GPU/overclocking GPU)
0x7E = Corrupted OS file, possibly from overclocking. Run sfc /scannow and chkdsk /r
This post has been edited by owikh84: Aug 8 2012, 06:41 AM


 Jan 8 2011, 12:42 AM, updated 12y ago
Jan 8 2011, 12:42 AM, updated 12y ago
 Quote
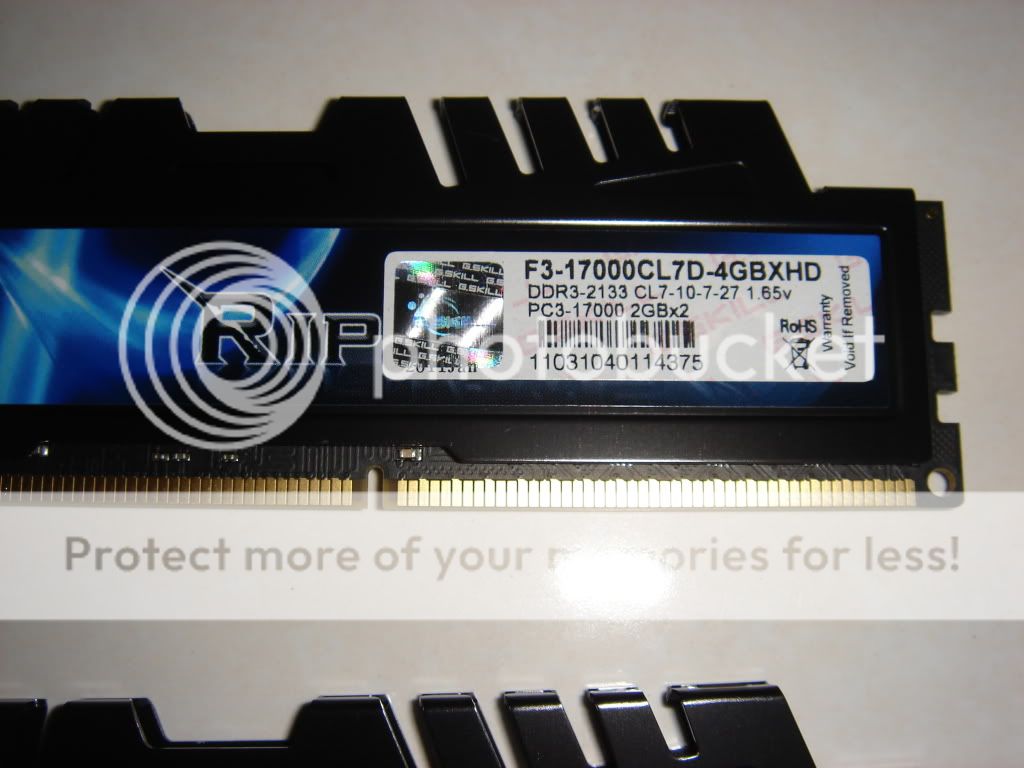
Quote



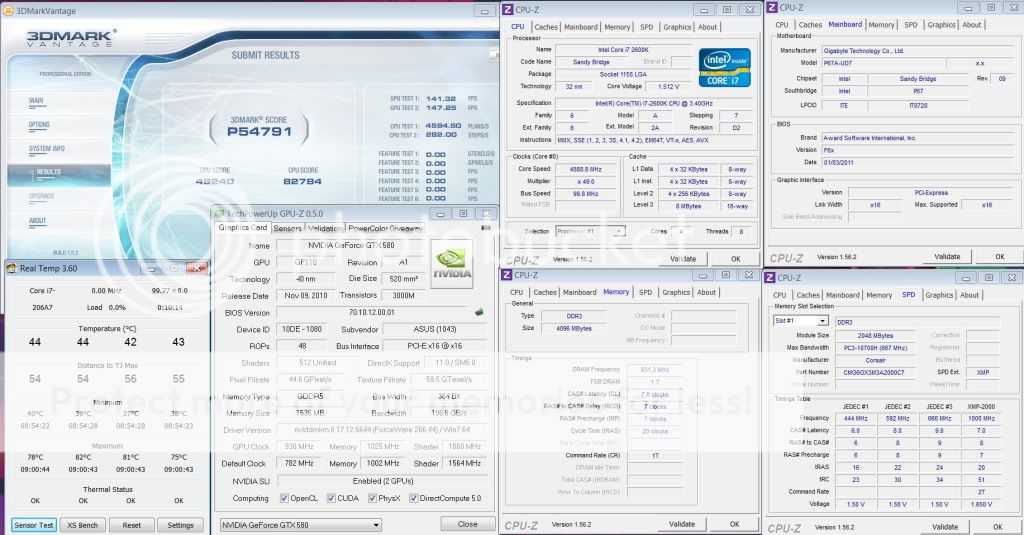
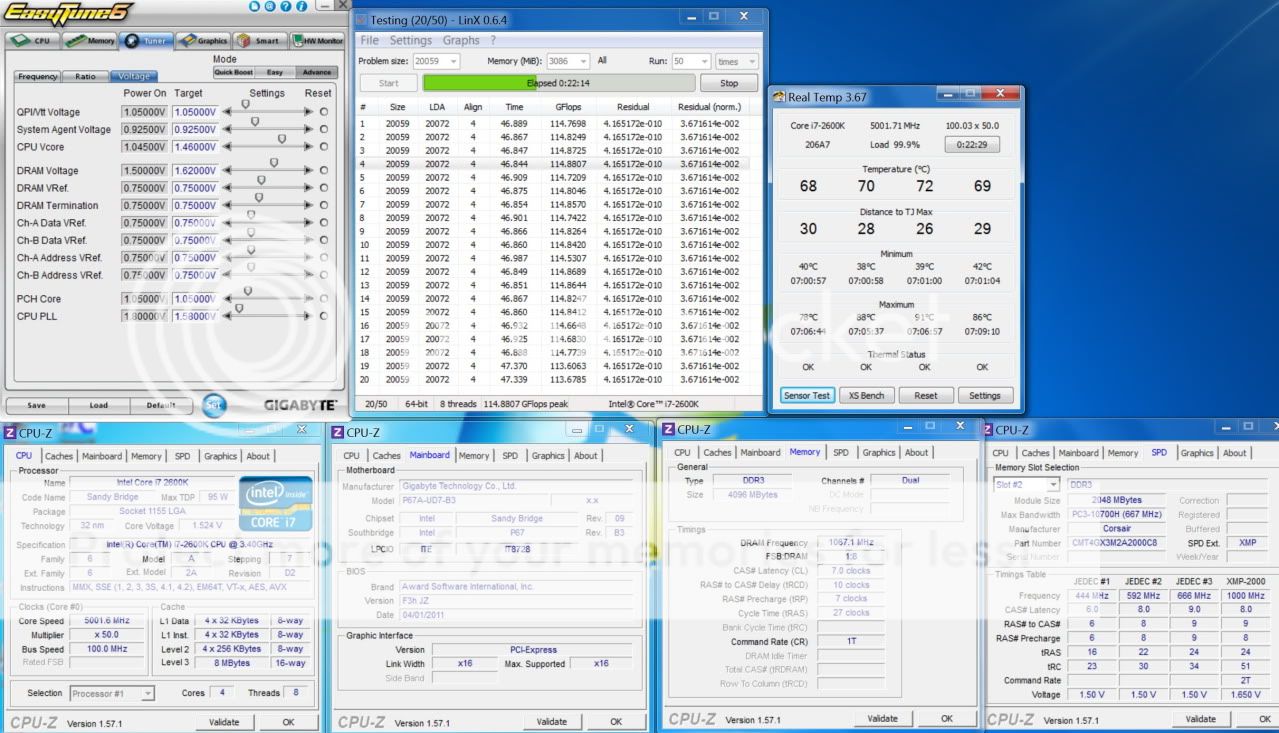


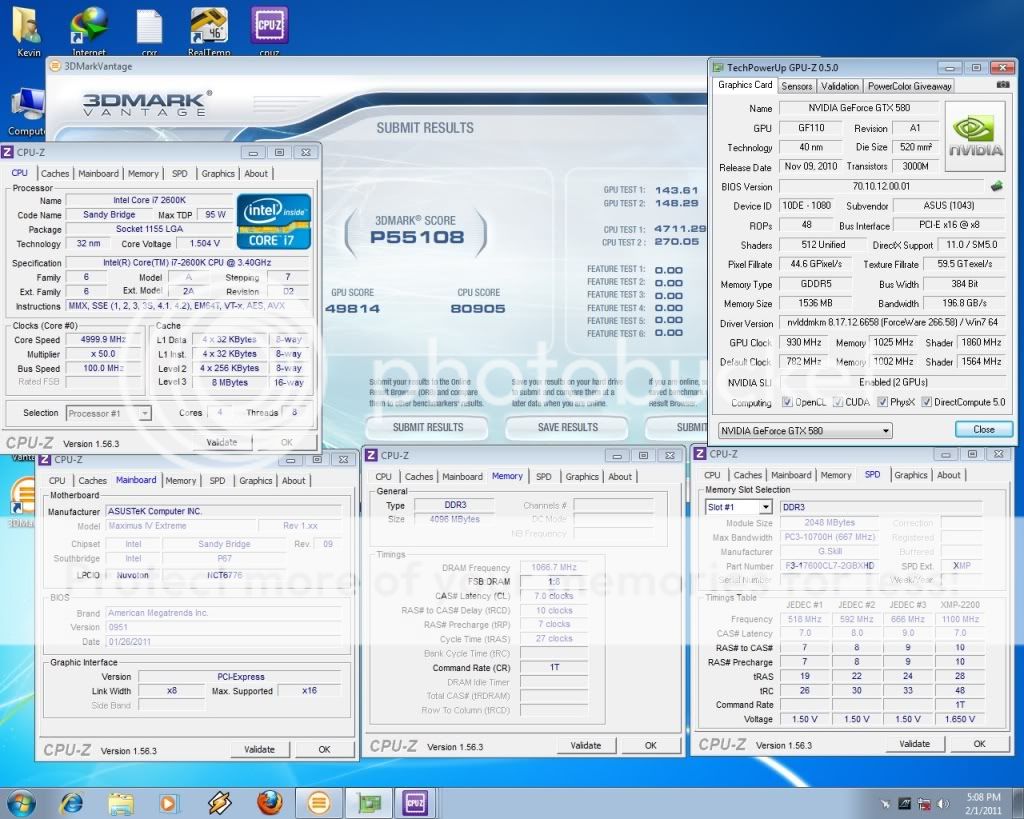
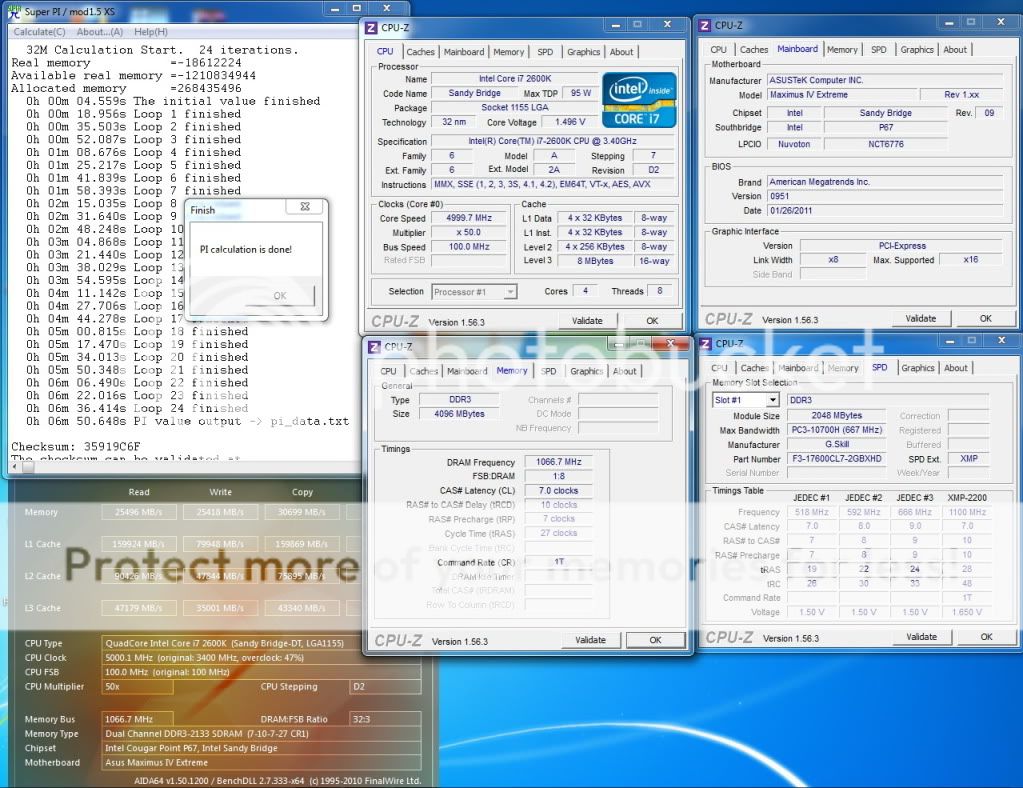













































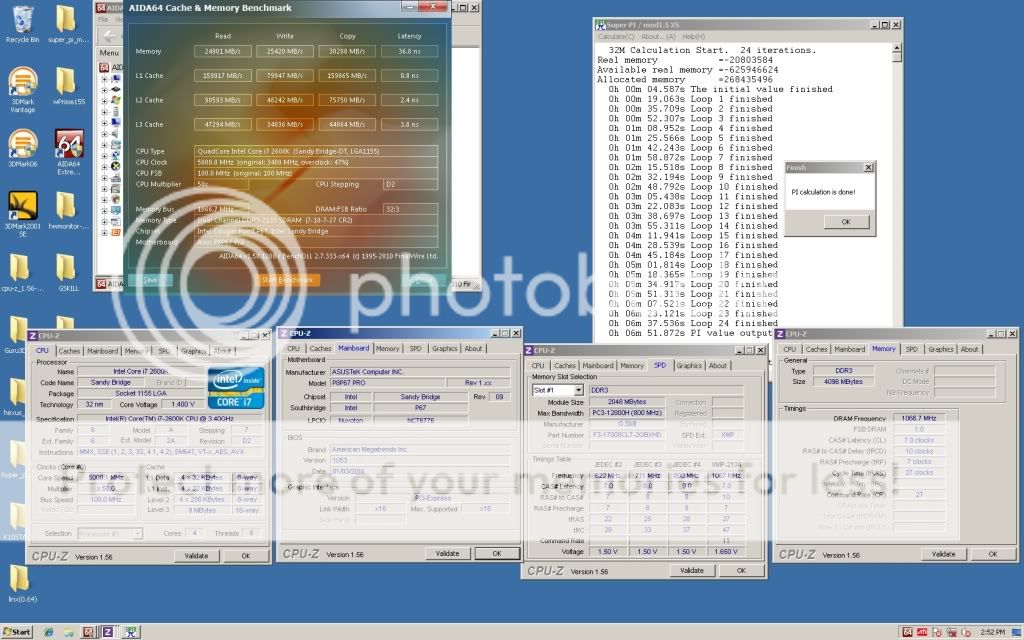


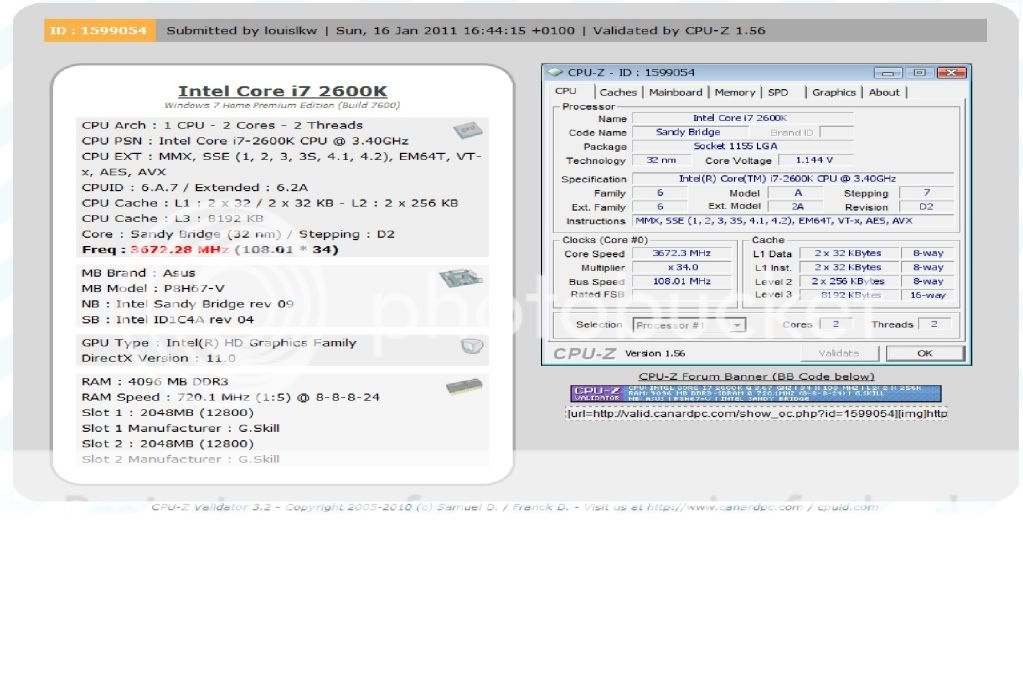







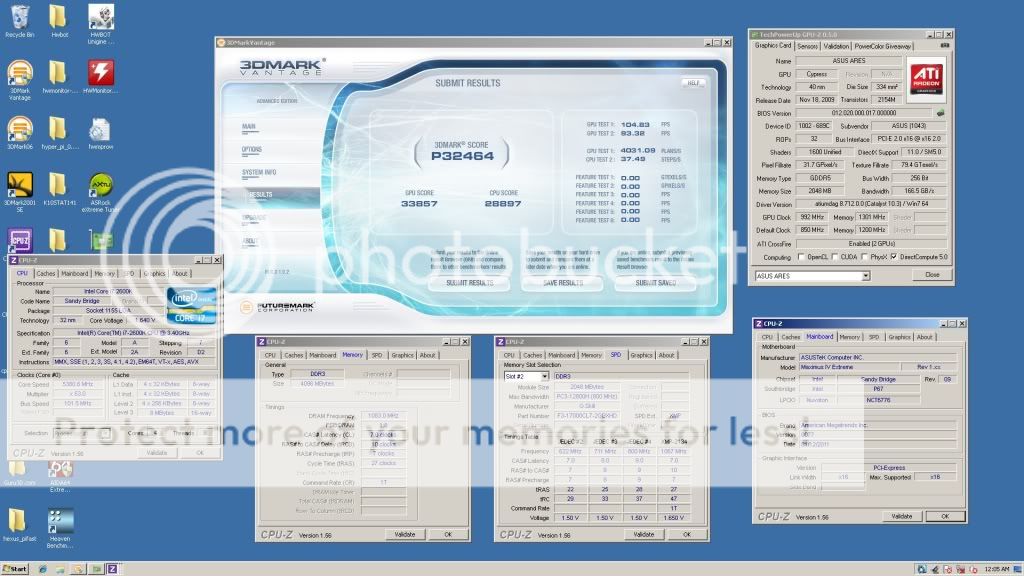










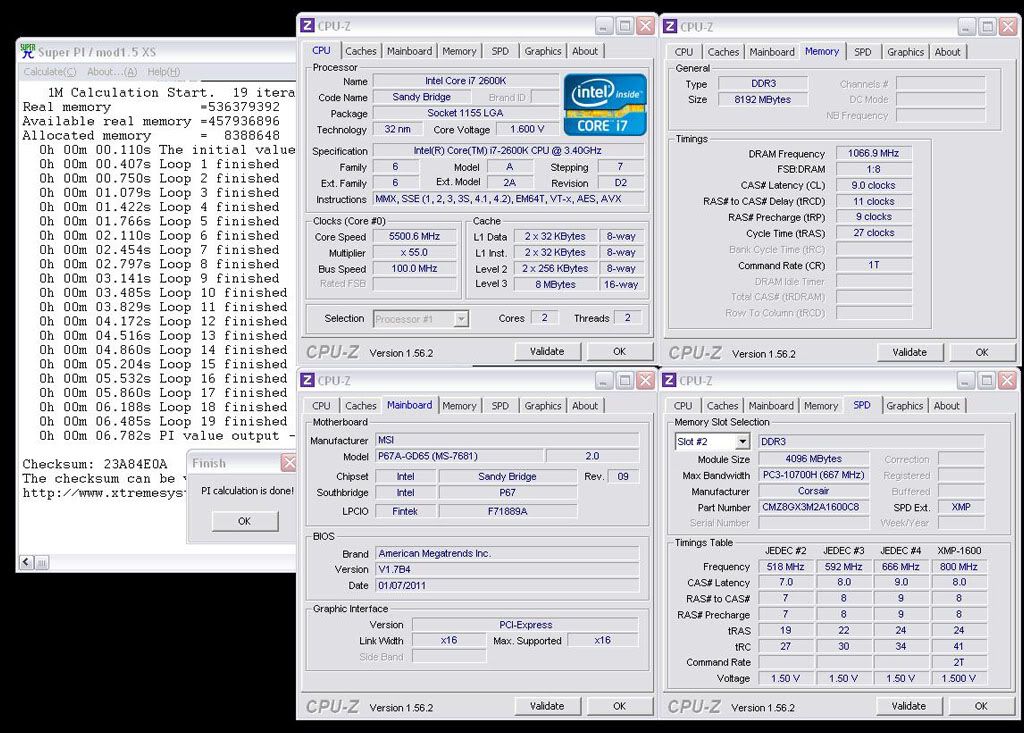
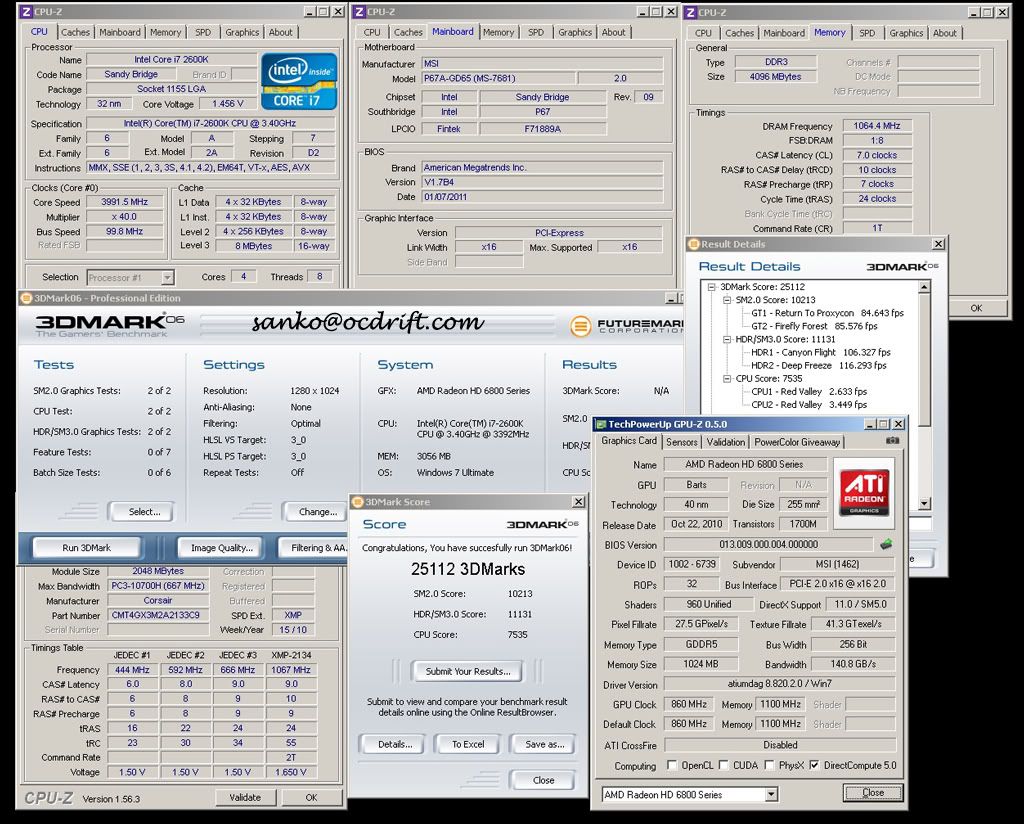



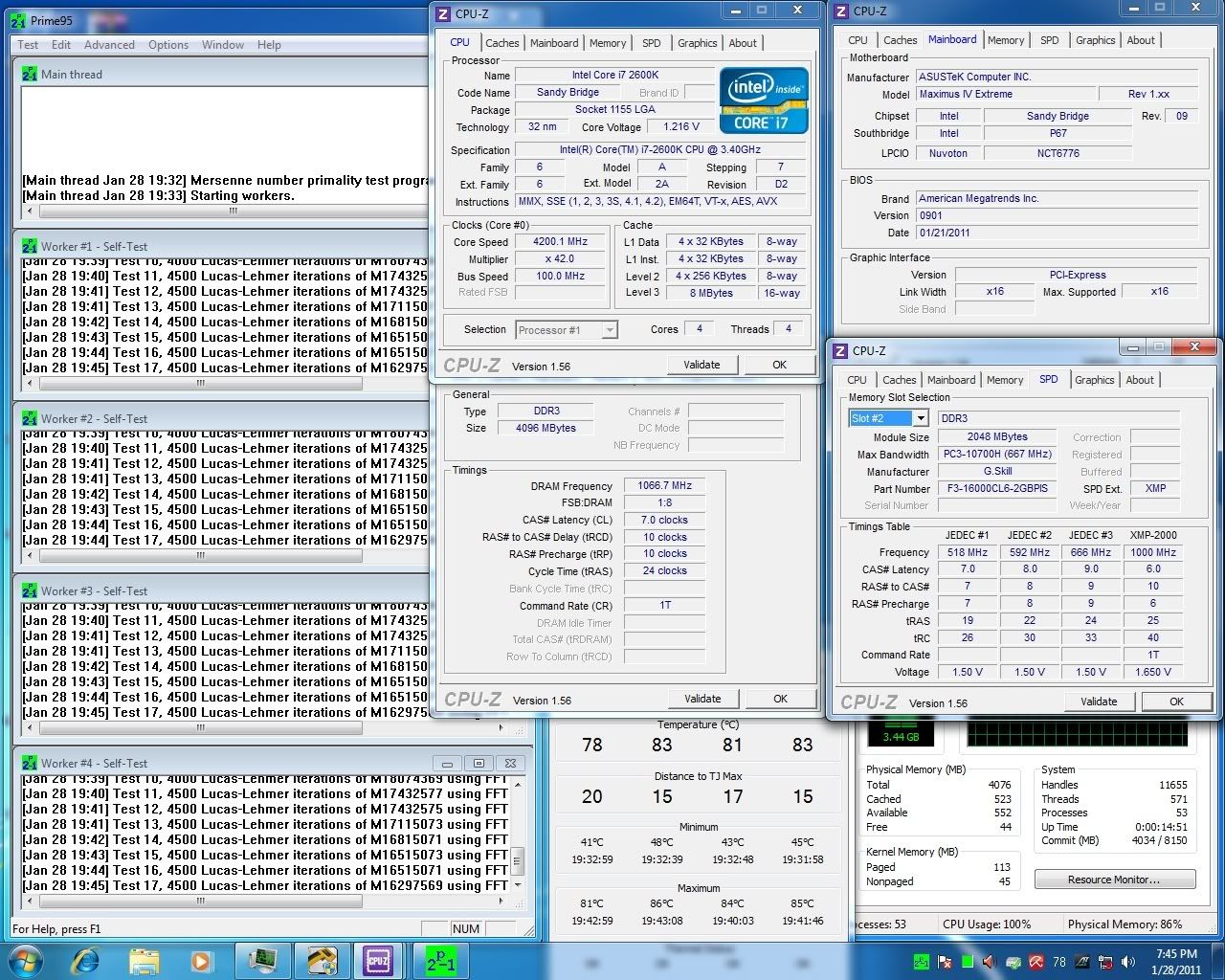

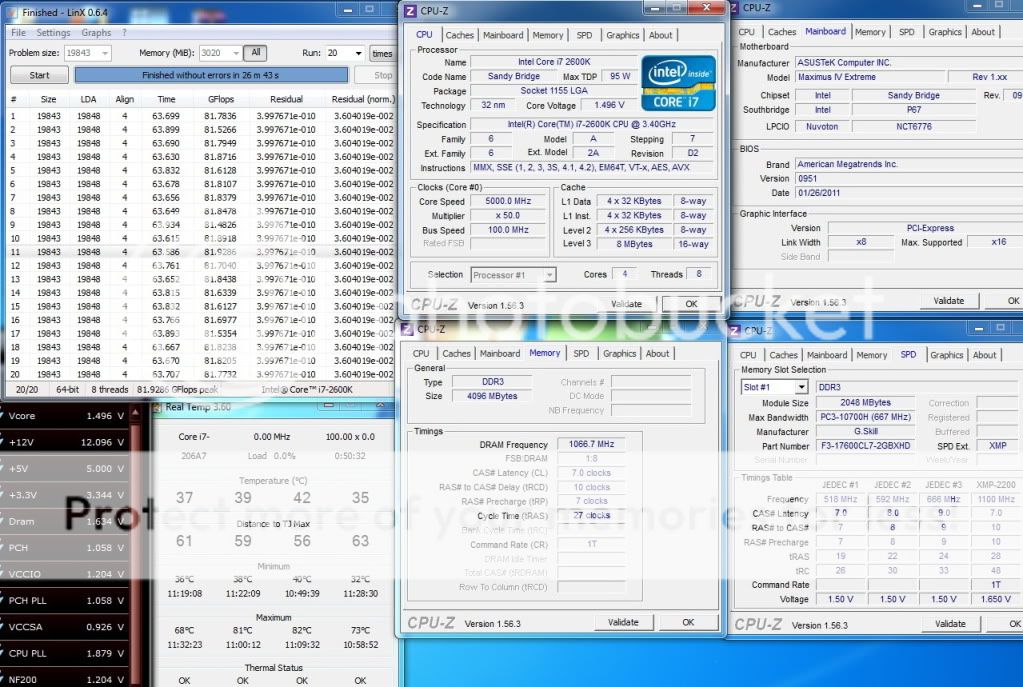
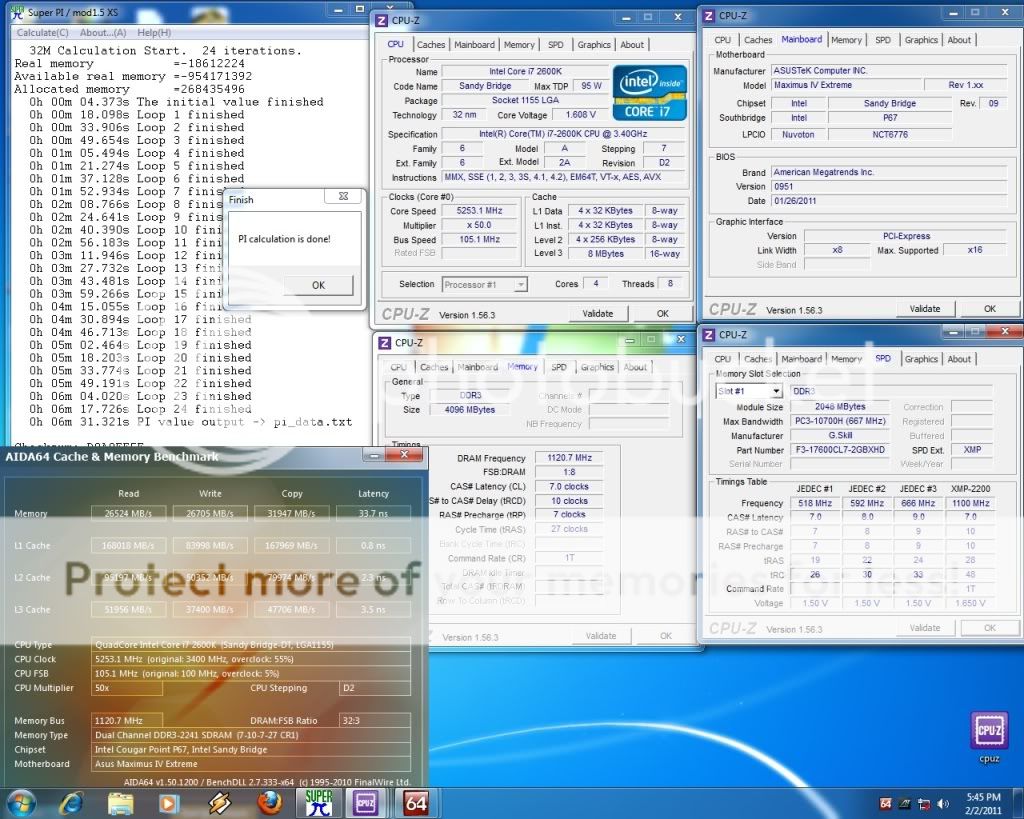
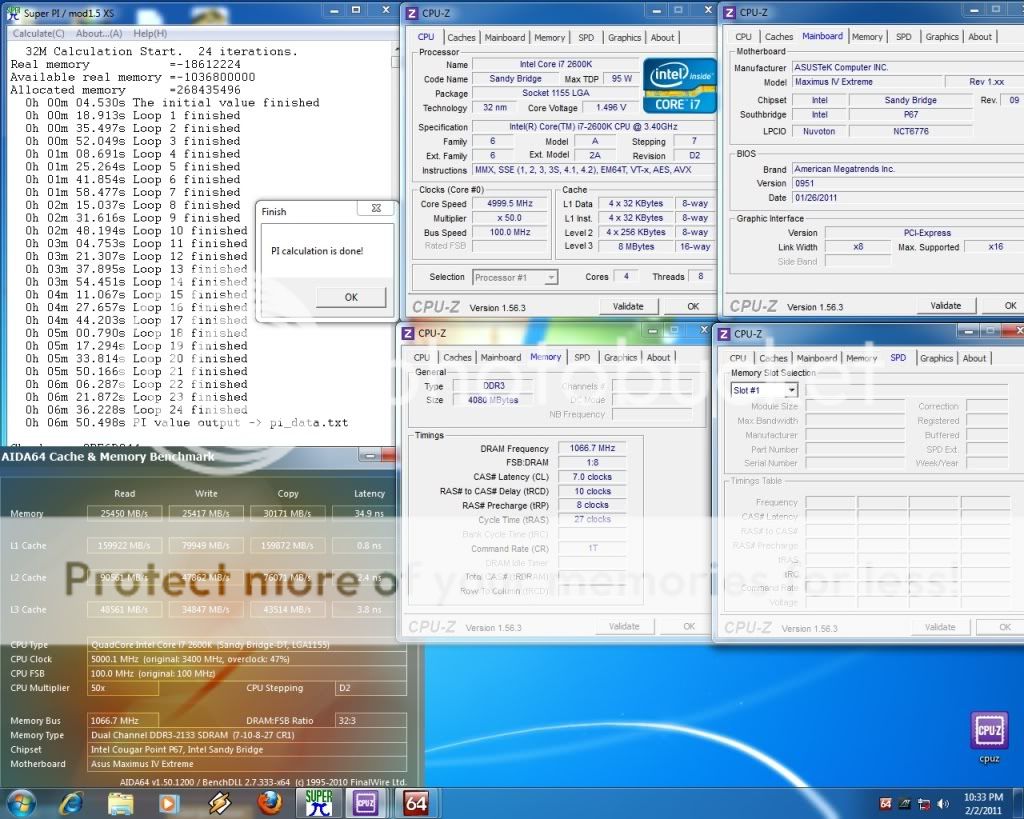
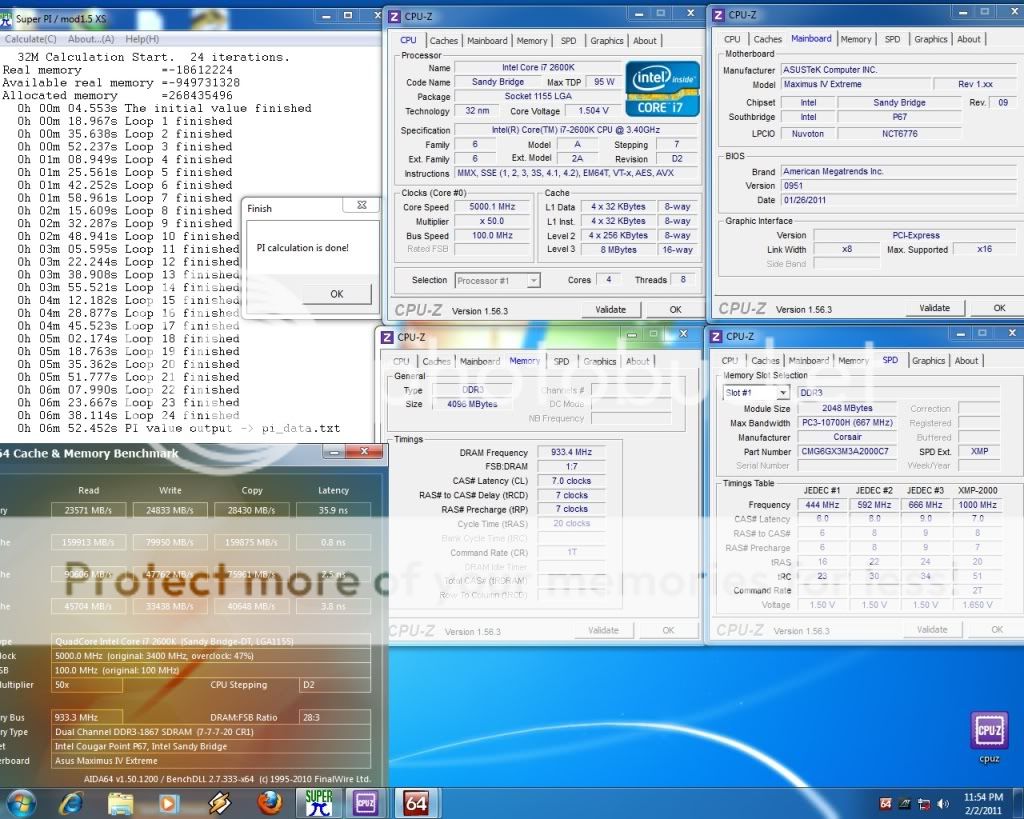


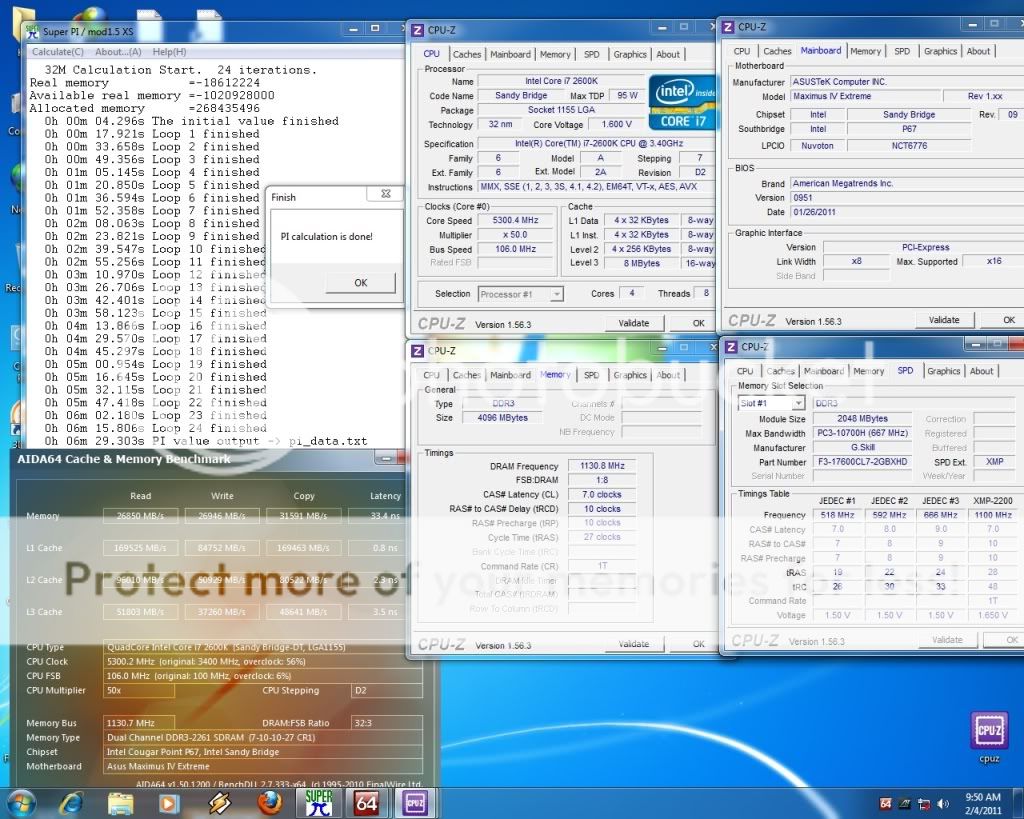
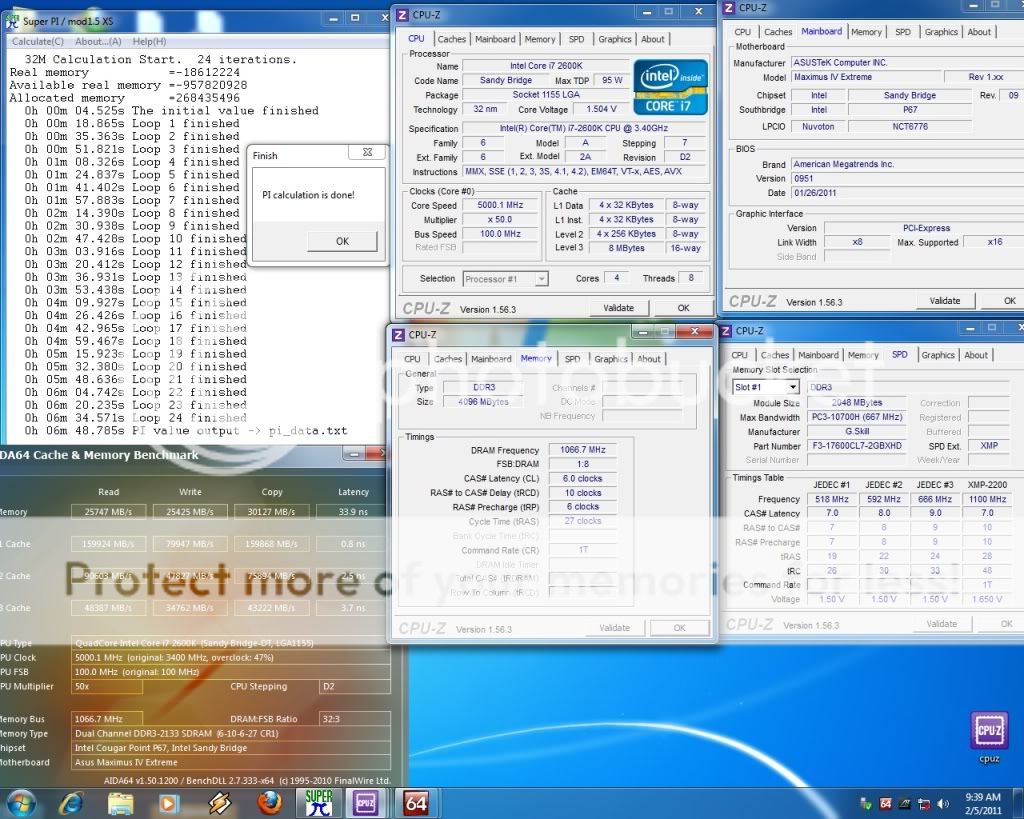
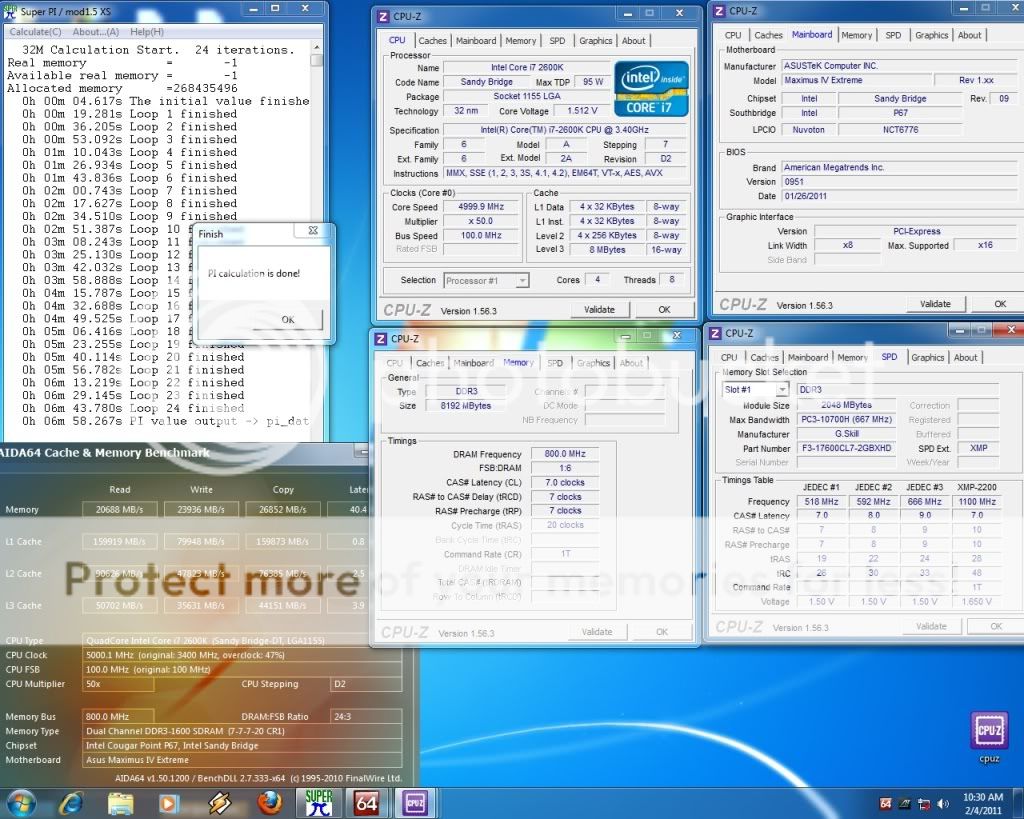
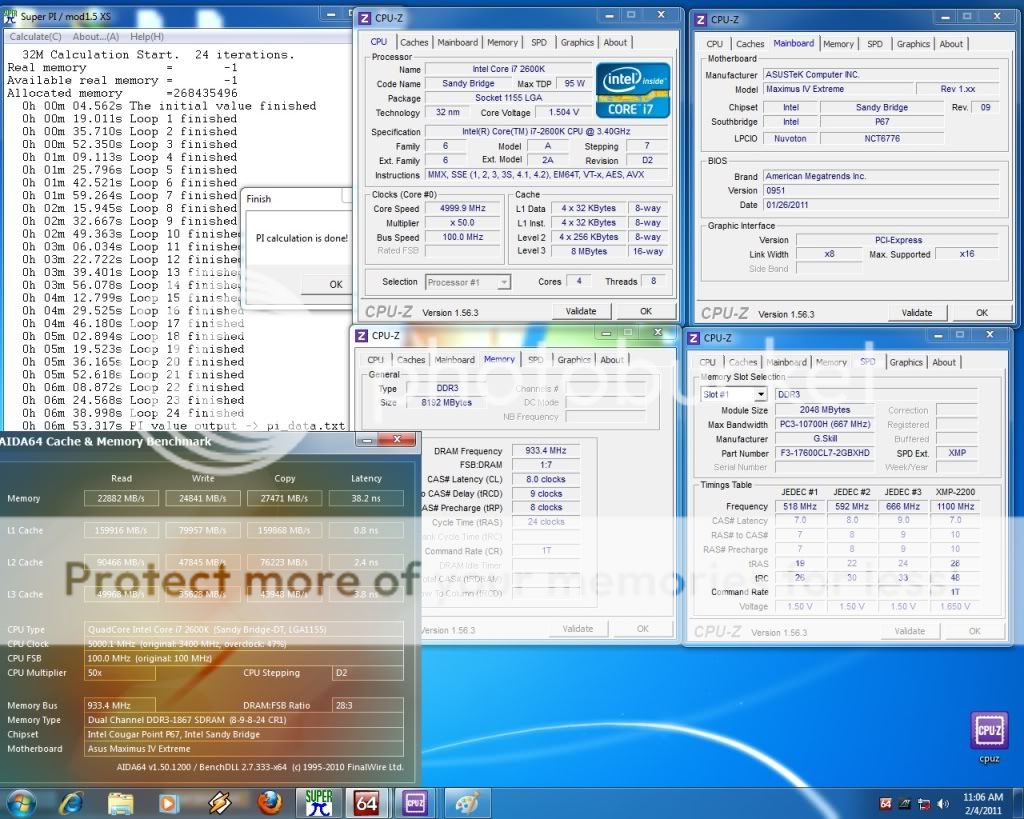
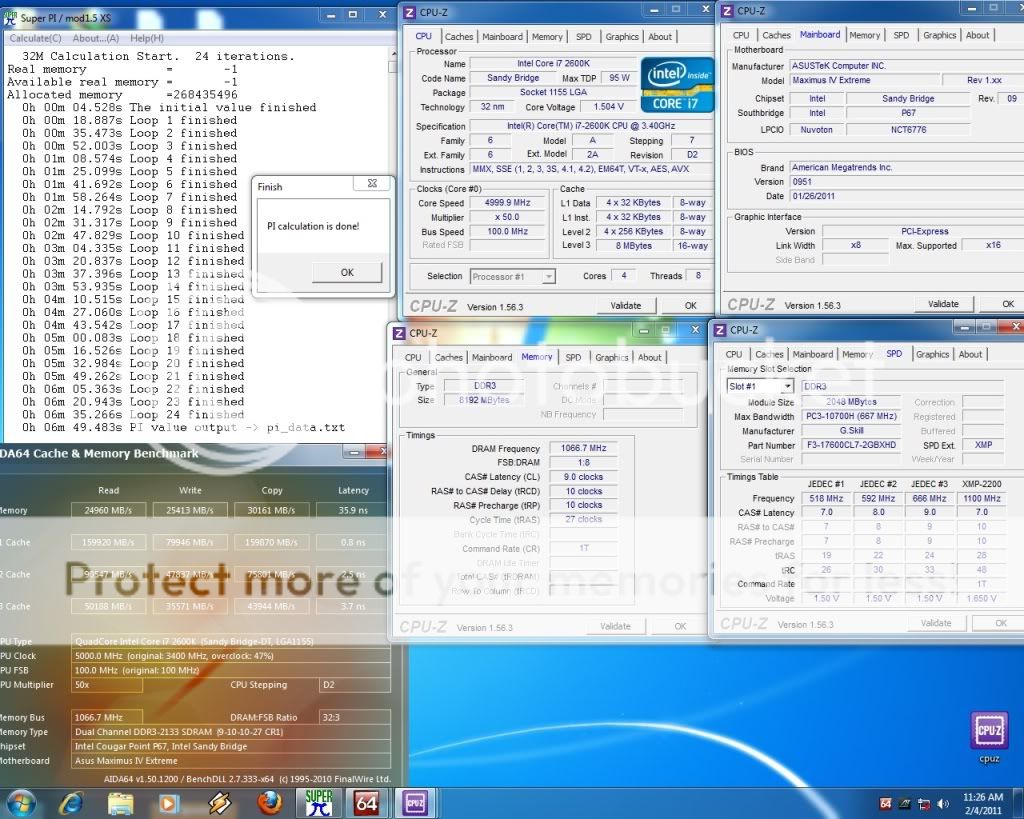


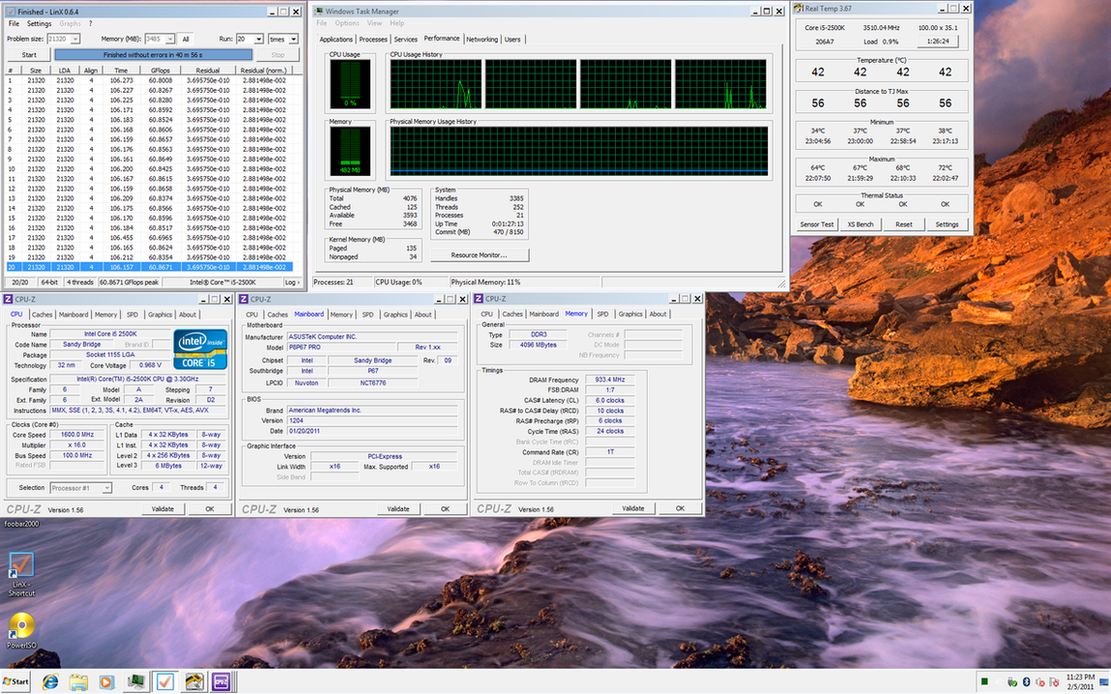




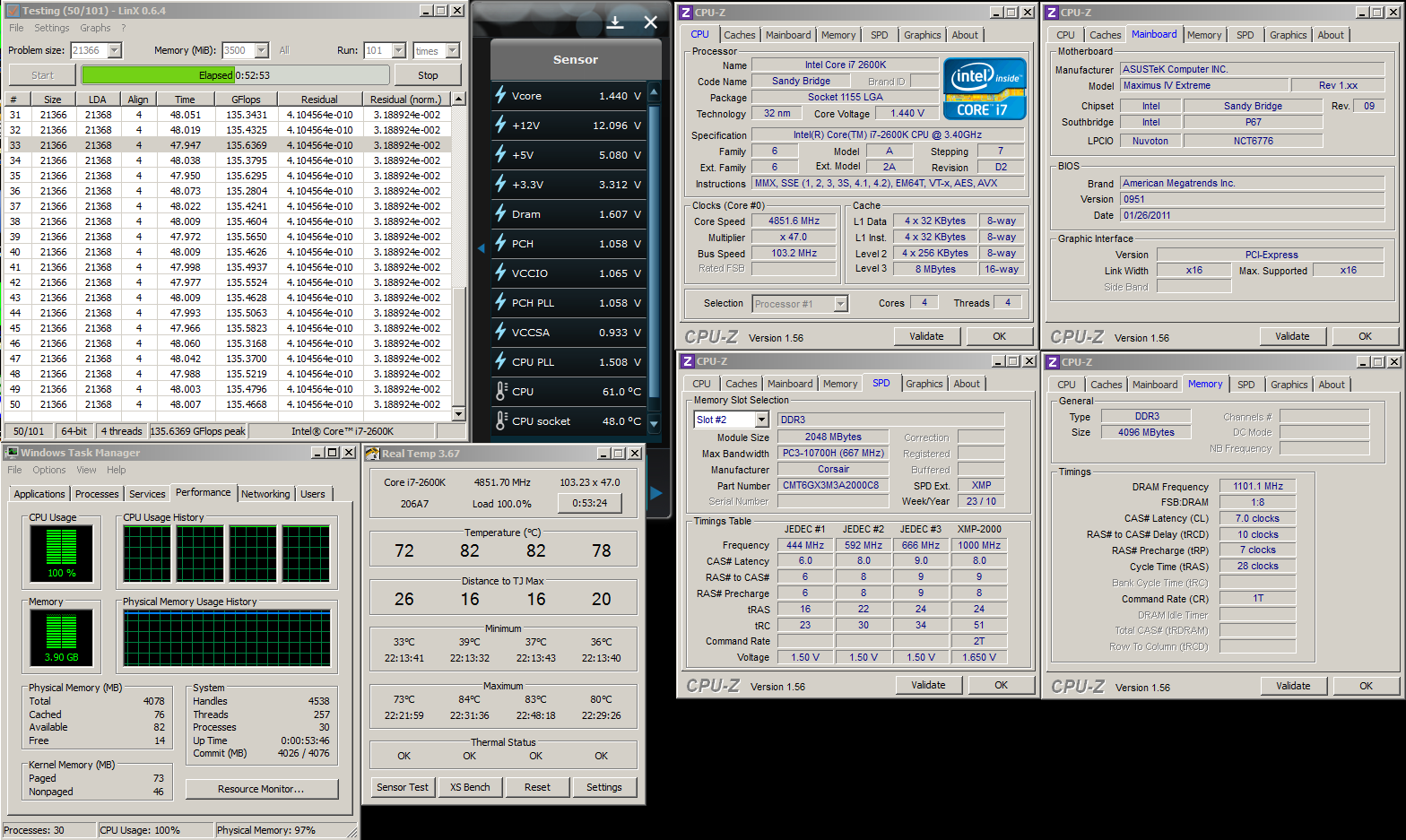
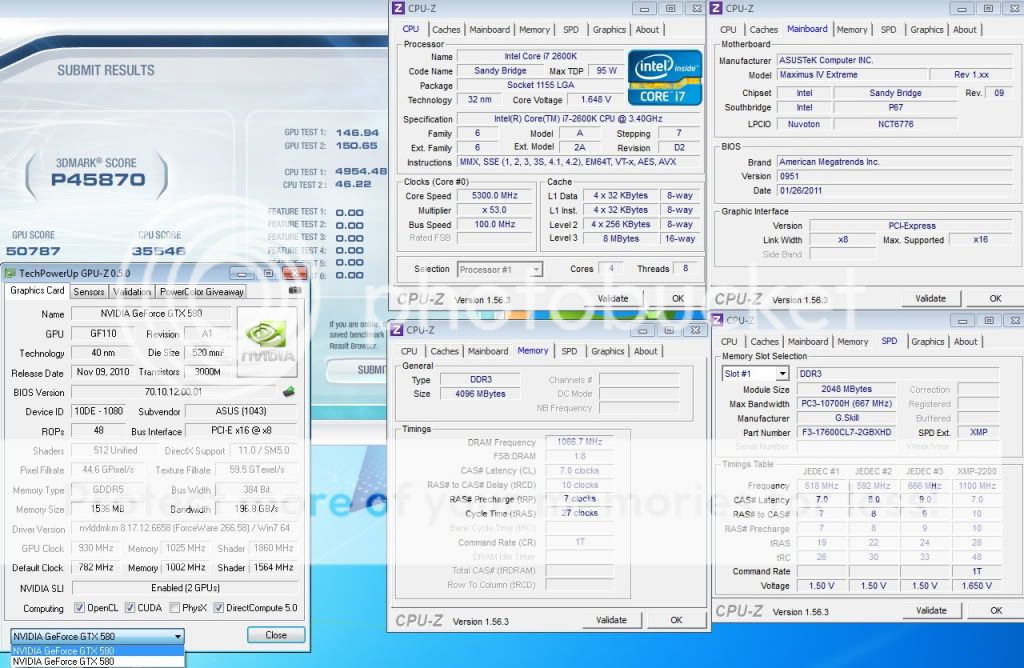












 0.2757sec
0.2757sec
 0.57
0.57
 6 queries
6 queries
 GZIP Disabled
GZIP Disabled