Official SSD Discussion Thread
Introduction
QUOTE
A solid-state drive (SSD) (sometimes improperly referred to as a "solid-state disk" or "electronic disk") is a data storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies as memory to store data persistently. SSD technology uses electronic interfaces compatible with traditional block input/output (I/O) hard disk drives. SSDs do not employ any moving mechanical components, which distinguishes them from traditional magnetic disks such as hard disk drives (HDDs) or floppy disks, which are electromechanical devices containing spinning disks and movable read/write heads. Compared with electromechanical disks, SSDs are typically less susceptible to physical shock, are silent, and have lower access time and latency, but are, at 2011 market prices, more expensive per unit of storage. The prices have continued to decline in 2012.
SSDs share the I/O interface technology developed for hard disk drives, thus permitting simple replacement for most applications.
As of 2010, most SSDs use NAND-based flash memory, which retains data without power. For applications requiring fast access, but not necessarily data persistence after power loss, SSDs may be constructed from random-access memory (RAM). Such devices may employ separate power sources, such as batteries, to maintain data after power loss.
Hybrid drives combine the features of SSDs and HDDs in the same unit, containing a large hard disk drive and an SSD cache to improve performance of frequently accessed data. These devices may offer near-SSD performance for many applications.
SSDs share the I/O interface technology developed for hard disk drives, thus permitting simple replacement for most applications.
As of 2010, most SSDs use NAND-based flash memory, which retains data without power. For applications requiring fast access, but not necessarily data persistence after power loss, SSDs may be constructed from random-access memory (RAM). Such devices may employ separate power sources, such as batteries, to maintain data after power loss.
Hybrid drives combine the features of SSDs and HDDs in the same unit, containing a large hard disk drive and an SSD cache to improve performance of frequently accessed data. These devices may offer near-SSD performance for many applications.
The benefits of using a SSD by Corsair
The SSD Optimization Guide
http://thessdreview.com/ssd-guides/optimiz...zation-guide-2/
SSD related Tools and Ultilities
HDDTune ~ http://www.hdtune.com/download.html
AS SSD Benchmark ~ http://alex-is.de/PHP/fusion/downloads.php...4&download_id=9
ATTO Disk Brench ~ http://www.attotech.com/products/product.p...=Disk_Benchmark
CrystalDiskMark ~ http://crystalmark.info/software/CrystalDi...rk/index-e.html
Intel SSD toolbox ~ http://downloadcenter.intel.com/Detail_Des...Y&DwnldID=18455
SSDlife ~ http://ssd-life.com/eng/download-ssdlife.html
SSD Performance Chart
All SSD Charts 2011 [benchmarks] - http://www.tomshardware.com/charts/ssd-cha...hmarks,129.html
All SSD RAID 0 Charts 2011 [benchmarks] - http://www.tomshardware.com/charts/ssd-rai...hmarks,120.html
Tom's Hardware's SSD Performance Hierarchy Chart - http://www.tomshardware.com/reviews/ssd-re...ark,3269-6.html
SSD Versus HDD: Power And Performance - http://www.tomshardware.com/reviews/ssd-re...ark,3269-7.html
SSD Reviews - http://www.techpowerup.com/forums/showthread.php?t=150954
Source:
http://www.anandtech.com/print/2829
http://benchmarkreviews.com/index.php?opti...d=444&Itemid=60
http://www.bit-tech.net/hardware/storage/2...sd-controller/1
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid-state_drive
Previous Thread
The Solid State Storage Thread
The SSD Thread V2, Faster Better Greener Unbreakable!
This post has been edited by rc2x: Apr 18 2013, 04:51 PM


 Aug 16 2012, 09:25 PM, updated 13y ago
Aug 16 2012, 09:25 PM, updated 13y ago
 Quote
Quote
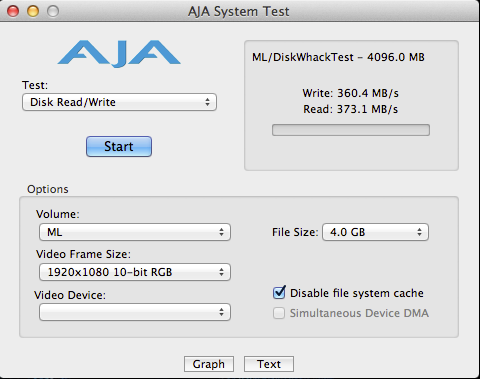
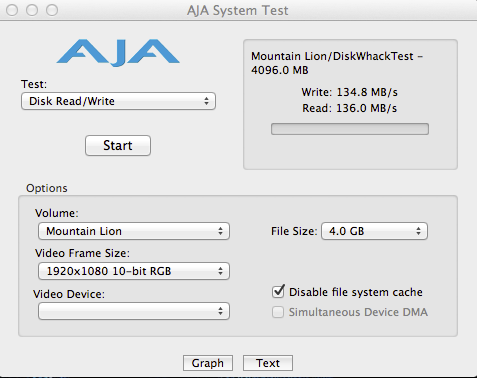
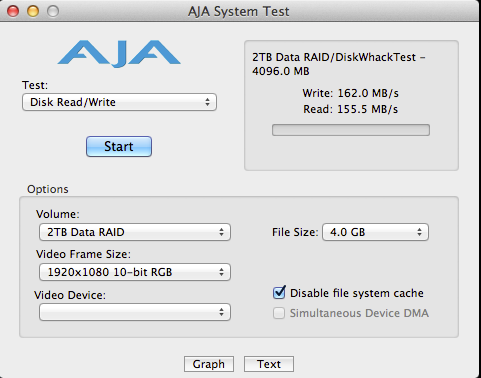
 0.0304sec
0.0304sec
 1.43
1.43
 6 queries
6 queries
 GZIP Disabled
GZIP Disabled