https://www.symbolab.com/http://onsolver.com/Original First Post» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
On August 5th, 2013,
maximR posted the problems of
International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) 2013 on SPM 2013 Thread. The problems are technically challenging, which most of them are not conventionally covered at SPM/STPM syllabus and some not even at university undergraduate level. Despite that, I managed to work out something for Problem 1. Hence, I'd like ask any Mathematician
to verify my workings and validate the proposed solution. You are welcome to provide alternative solution as well.
Thank you & Have a nice day!



From now on, you can post your questions about math, physics, or anything else you can think of on this thread. While I’ll do my best to answer them as precisely and reasonably necessary as possible when I’m not busy, it’s best to keep in mind that
to err is human.

» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
P. Prerequisites
1. Equations and Inequalities
2. Coordinates and Graphs
3. Functions
4. Polynomial and Rational Functions
5. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
6. Systems of Equations and Inequalities
7. Matrices and Determinants
8. Conic Sections
9. Sequences and Series
10. Counting and Probability
Calculus :: Early Transcendentals» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
1. Functions and Models
2. Limits and Derivatives
3. Differentiation Rules
4. Applications of Differentiation
5. Integrals
6. Applications of Integration
7. Techniques of Integration
8. Further Applications of Integration
9. Differential Equations
10. Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
11. Infinite Sequences and Series
12. Vectors and the Geometry of Space
13. Vector Functions
14. Partial Derivatives
15. Multiple Integrals
16. Vector Calculus
17. Second-Order Differential Equations
Advanced Engineering Mathematics» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
Complex Analysis
- Complex Numbers
- Complex Functions
- Complex Series and Theory of Residues
Determinants and Matrices
- Determinants
- Matrix Algebra
- Eigenvalue Problems of Matrices
Vector Analysis
- Vectors
- Vector Calculus
- Curved Coordinates
- Vector Transformation and Cartesian Tensors
Differential Equations and Laplace Transforms
- Ordinary Differential Equations
- Laplace Transforms
Fourier Analysis
- Fourier Series
- Fourier Transforms
Sturm–Liouville Theory and Special Functions
- Orthogonal Functions and Sturm–Liouville Problems
- Bessel and Legendre Functions
Partial Differential Equations
- Partial Differential Equations in Cartesian Coordinates
- Partial Differential Equations with Curved Boundaries
Variational Methods
- Calculus of Variation
Numerical Methods (a.k.a. Computational Methods for Applied Sciences)» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
Roots of Equations
- Bracketing Methods (Bisection Method, False-Position Method)
- Open Methods (Newton-Raphson Method, Secant Method)
- Roots of Polynomials
Linear Algebraic Equations
- Gauss Elimination
- LU Decomposition and Matrix Inversion
- Special Matrices and Gauss-Seidel
Optimization
- One-Dimensional Unconstrained Optimization
- Multidimensional Unconstrained Optimization
- Constrained Optimization
Curve-Fitting
- Least-Squares Regression
- Interpolation
- Fourier Approximation
Numerical Differentiation & Integration
- Newton-Cotes Integration Formulas
- Integration of Equations
- Numerical Differentiation
Ordinary Differential Equations
- Runge-Kutta Methods
- Stiffness and Multistep Methods
- Boundary-Value and Eigenvalue Problems
Partial Differential Equations
- Finite Difference: Elliptic Equations
- Finite Difference: Parabolic Equations
- Finite-Element Method
Euler Angles» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
When reference frame F1 <i', j', k'> is obtained from frame F0 <i, j, k> by a rotation about the z-axis, the associated rotation matrix is
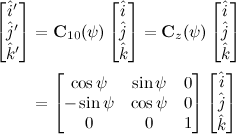
For a rotation about the y-axis,
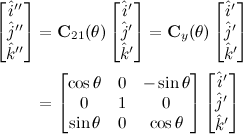
For a rotation about the x-axis,
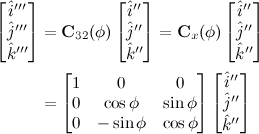
Euler rotation is a very common choice in aerospace applications, and is called a 3-2-1 attitude sequence, and is depicted in Figure below.

The terminology relates to the order of rotations. A principal z-axis (labeled 3) rotation is first, followed by a principal y-axis (labeled 2) rotation, followed by a principal x-axis (labeled 1) rotation. In this case, the rotation matrix from frame F1 to frame F2 is given by
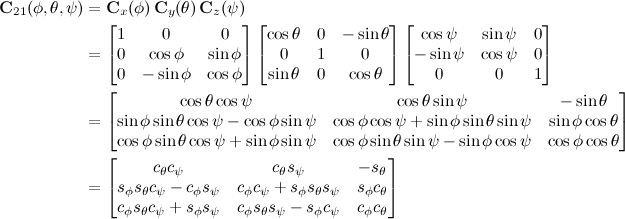
A more complicated coordinate transformation can be derived by multiple single-axis rotations in a given sequence, using the elementary rotation matrices, as demonstrated below.
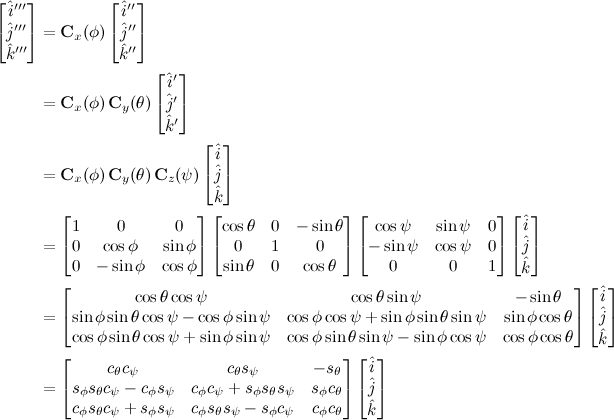
Operators & Symbols ::
(–x, y) ± + − × ÷ √ ² ³ ^ ∫ Σ Δ ∇ ∂ ∠ ° Ω “” → ← ↑ ↓ ∵ ∴ ½ ∞ ≈ ≠ ≪ ≤ ≥ ≫ • · ∝ † ⊗ ✔ ✘ 2⁄2 x≈-1.25992 ∧ ‖a‖ y≈-1.5874 …
Common Greek alphabets in Rotational dynamics:
ϕ, θ, ψ, ω
PID Controller ::u = − (Ki*∫ x + Kp*x + Kd*ẋ)
| 15° | π/12 |
| 30° | π/6 |
| 45° | π/4 |
| 60° | π/3 |
| 75° | 5π/12 |
| 90° | π/2 |
① ② ③ ④ ⑤ ⑥ ⑦ ⑧ ⑨ ⑩
b² – 4
acSuperscripts and subscripts ::
x⁰ x¹ x² x³ x⁴ x⁵ x⁶ x⁷ x⁸ x⁹ x⁺ x⁻ x⁼ x⁽ ⁾ xⁿ x* x˙ xˣ
x₀ x₁ x₂ x₃ x₄ x₅ x₆ x₇ x₈ x₉ x₊ x₋ x₌ x₍ ₎ xᵢ xᵣ xₑ xₙ
Greek alphabets (lowercase) ::
α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ, η, θ, κ, λ, μ, ξ, π, ρ, σ, τ, υ, ϕ, φ, χ, ψ, ω
Greek alphabets (uppercase & lowercase) ::
| Αα Alpha | Νν Nu |
| Ββ Beta | Ξξ Xi |
| Γγ Gamma | Οο Omicron |
| Δδ Delta | Ππ Pi |
| Εε Epsilon | Ρρ Rho |
| Ζζ Zeta | Σσς Sigma |
| Ηη Eta | Ττ Tau |
| Θθ Theta | Υυ Upsilon |
| Ιι Iota | Φϕφ Phi |
| Κκ Kappa | Χχ Chi |
| Λλ Lambda | Ψψ Psi |
| Μμ Mu | Ωω Omega |
» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
[attachmentid=4328645]
This post has been edited by Critical_Fallacy: Apr 29 2023, 03:50 PM 

 Aug 6 2013, 07:47 PM, updated 3y ago
Aug 6 2013, 07:47 PM, updated 3y ago

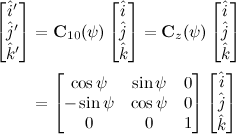
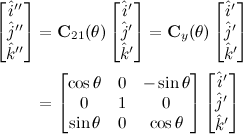
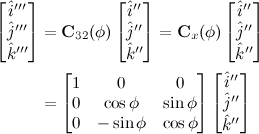

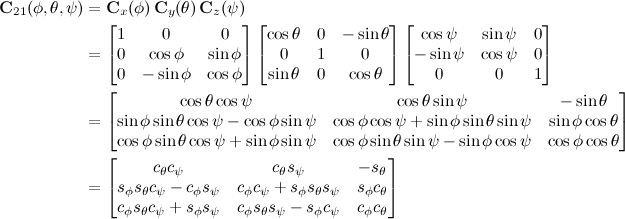

 Quote
Quote



 --->
---> 
 0.0365sec
0.0365sec
 0.64
0.64
 6 queries
6 queries
 GZIP Disabled
GZIP Disabled