This thread is to discuss about Intel Core i7 LGA1366 & X58 overclocking.
Please share your benchmark, stability test, guides etc...
» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
LGA1156/P55/H55/H57 vs LGA1366/X58

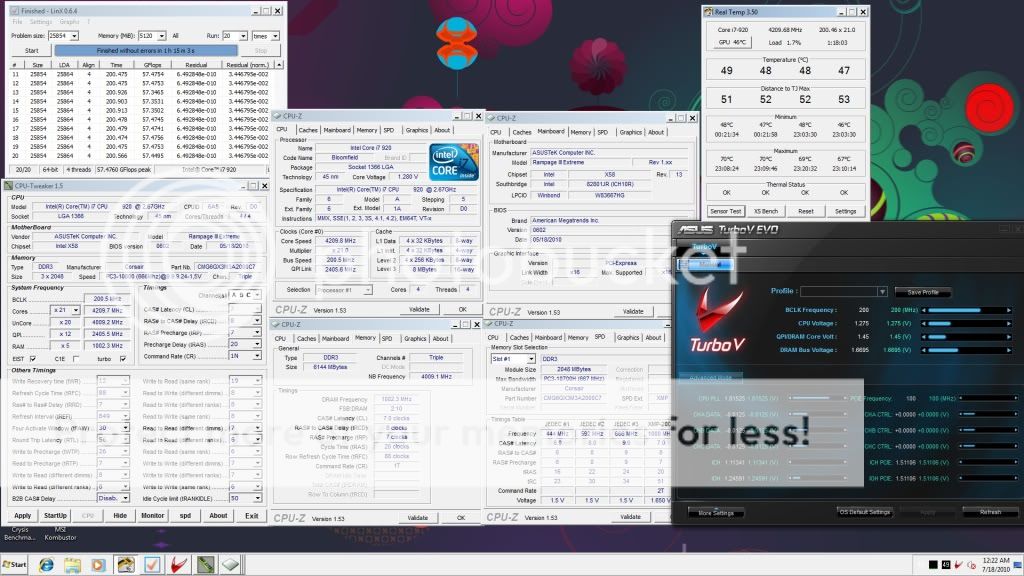
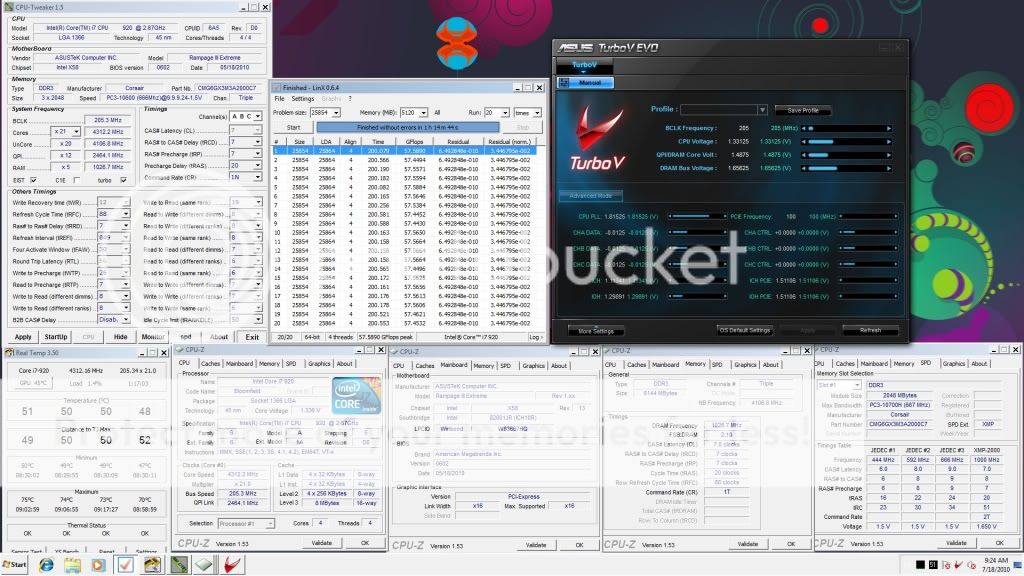
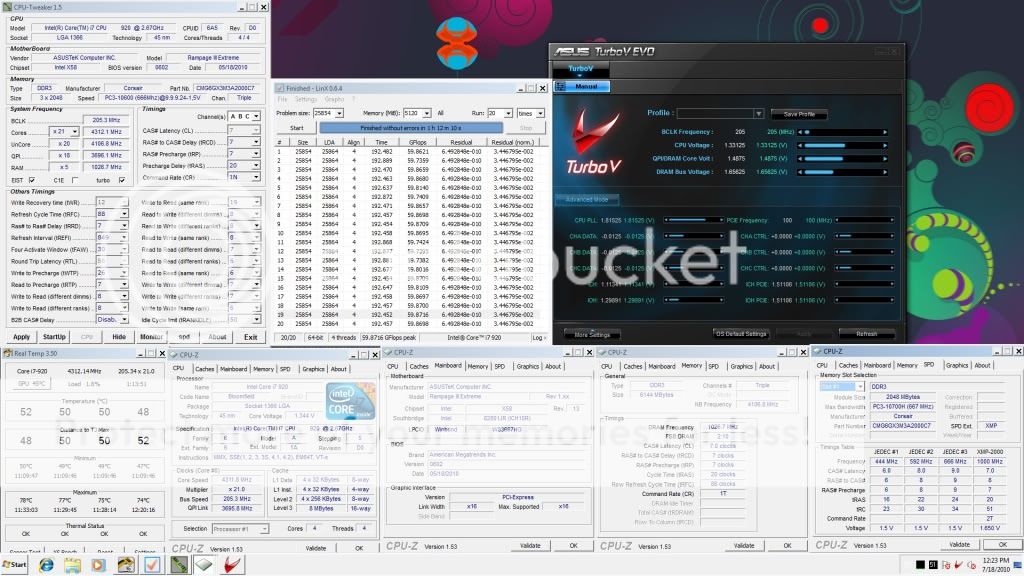
BCLK (Base Clock) - To keep things as simple as possible, this is the setting that we will be increasing to achieve our desired overclock. The default value for our 920 processor is 133.
QPI (Quick Path Interconnect) - The QPI connects the processor to the In Out Hub (IOH) - In other words, it is the way that your processor talks to the rest of your system.
Multipliers (Multis) and Dividers - As with previous platforms, i7 uses multipliers and dividers, but the way that i7 differs is that there are several of them for various things. For example, your CPU has a default multiplier (Multi) of 21x and there is a multiplier for the memory and the UnCore
UnCore - This is simply any part of the processor that is not the core, such as the memory controller or cache
Turbo Mode - is quite a complex feature, but to sum it up, if enabled, it will give you an extra multi, so on our 920, we get 21x instead of 20x
Vcore - This is just another term for the main CPU Voltage.
Software:
CPU-Z 1.59
LinX 0.6.4 - 10.3.9.015
Intel BurnTest 2.52
RealTemp 3.66 - works for 6 cores
CoreTemp 1.0 RC2
HWiNFO32 3.70
Prime95 32-Bit 27.1
Prime95 64-Bit 27.1
SuperPI Mod XS 1.5
HyperPI 0.99 Beta
AIDA64 2.00.1700
Cinebench 11.5
Here are some links you may find useful:
- Intel Core i7 Specifications
- Ultimate Core i7 Overclocking Guide
- from X-bit labs
- Guide to Overclocking the Core I7 920 to 4.0Ghz
- Intel I7 & X58 oc and discussion thread V1
DDR3 IC

BSOD codes for overclocking:
QUOTE
0x101 = increase vcore
0x124 = increase vcore
0x0A = unstable RAM/IMC, increase QPI first, if that doesn't work increase vcore
0x1E = increase vcore
0x3B = increase vcore
0x3D = increase vcore
0xD1 = QPI/VTT, increase/decrease as necessary, can also be unstable Ram, raise Ram voltage
0x9C = QPI/VTT most likely, but increasing vcore has helped in some instances
0x50 = RAM timings/Frequency or uncore multi unstable, increase RAM voltage or adjust QPI/VTT, or lower uncore if you're higher than 2x
0x109 = Not enough or too Much memory voltage
0x116 = Low IOH (NB) voltage, GPU issue (most common when running multi-GPU/overclocking GPU)
0x7E = Corrupted OS file, possibly from overclocking. Run sfc /scannow and chkdsk /r
0x124 = increase vcore
0x0A = unstable RAM/IMC, increase QPI first, if that doesn't work increase vcore
0x1E = increase vcore
0x3B = increase vcore
0x3D = increase vcore
0xD1 = QPI/VTT, increase/decrease as necessary, can also be unstable Ram, raise Ram voltage
0x9C = QPI/VTT most likely, but increasing vcore has helped in some instances
0x50 = RAM timings/Frequency or uncore multi unstable, increase RAM voltage or adjust QPI/VTT, or lower uncore if you're higher than 2x
0x109 = Not enough or too Much memory voltage
0x116 = Low IOH (NB) voltage, GPU issue (most common when running multi-GPU/overclocking GPU)
0x7E = Corrupted OS file, possibly from overclocking. Run sfc /scannow and chkdsk /r
This post has been edited by owikh84: Feb 25 2012, 10:08 PM


 Aug 31 2010, 01:52 PM, updated 12y ago
Aug 31 2010, 01:52 PM, updated 12y ago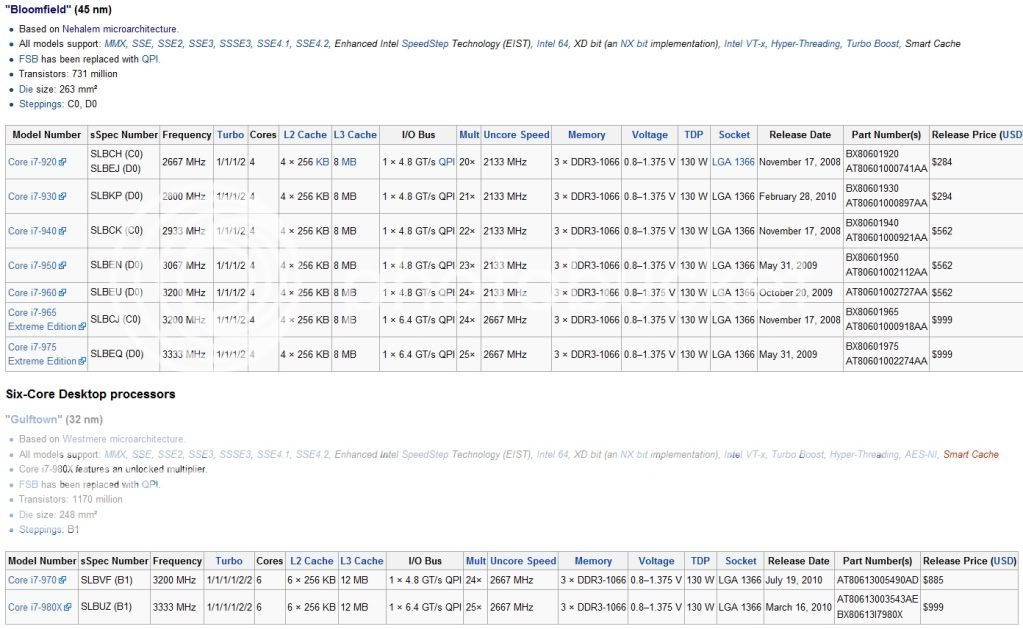
 Quote
Quote












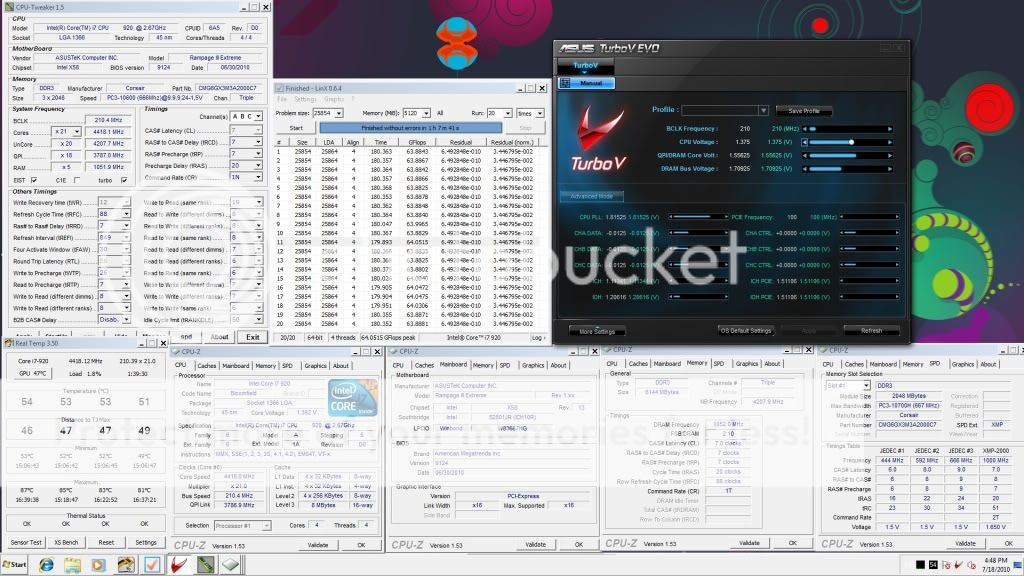





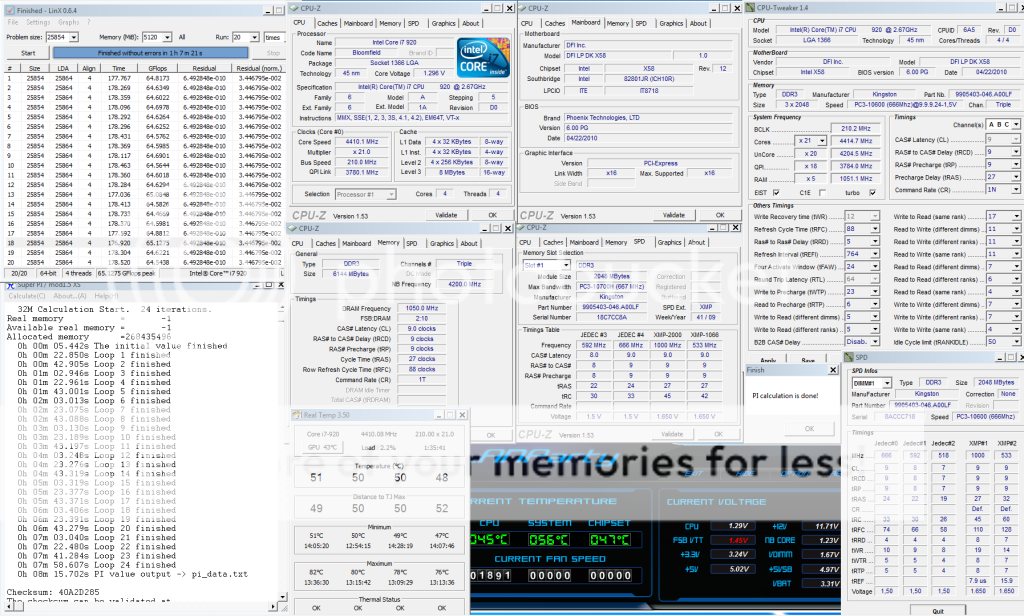


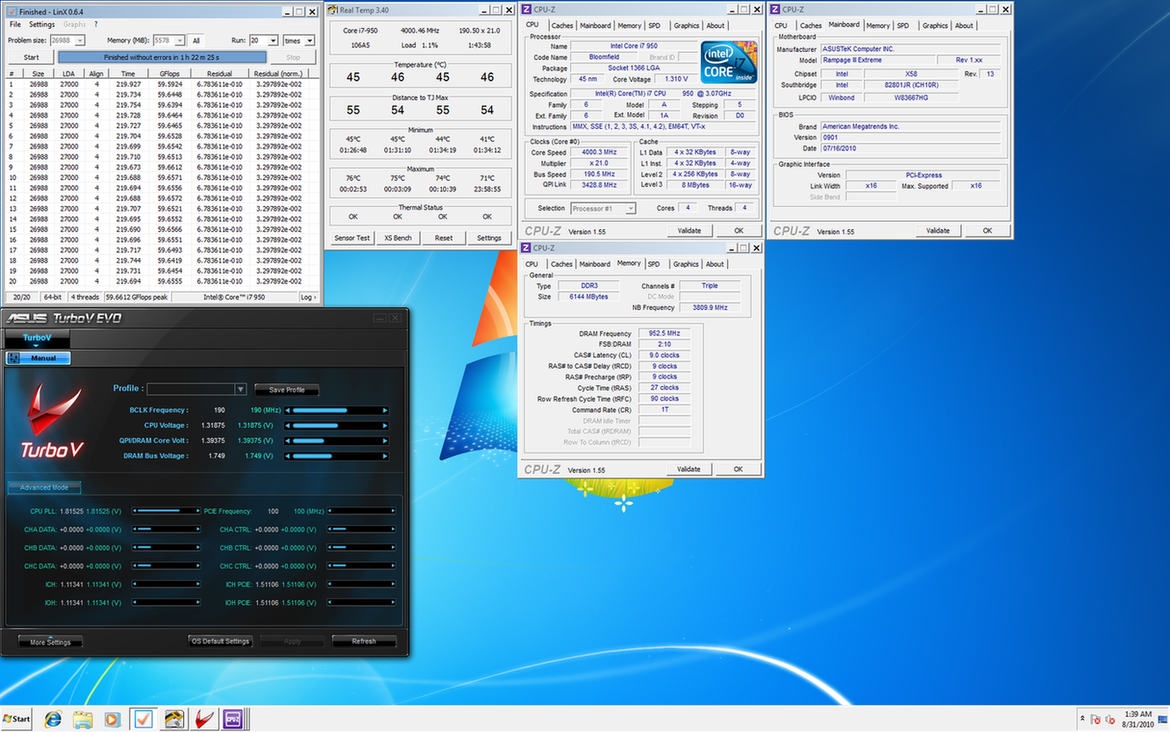
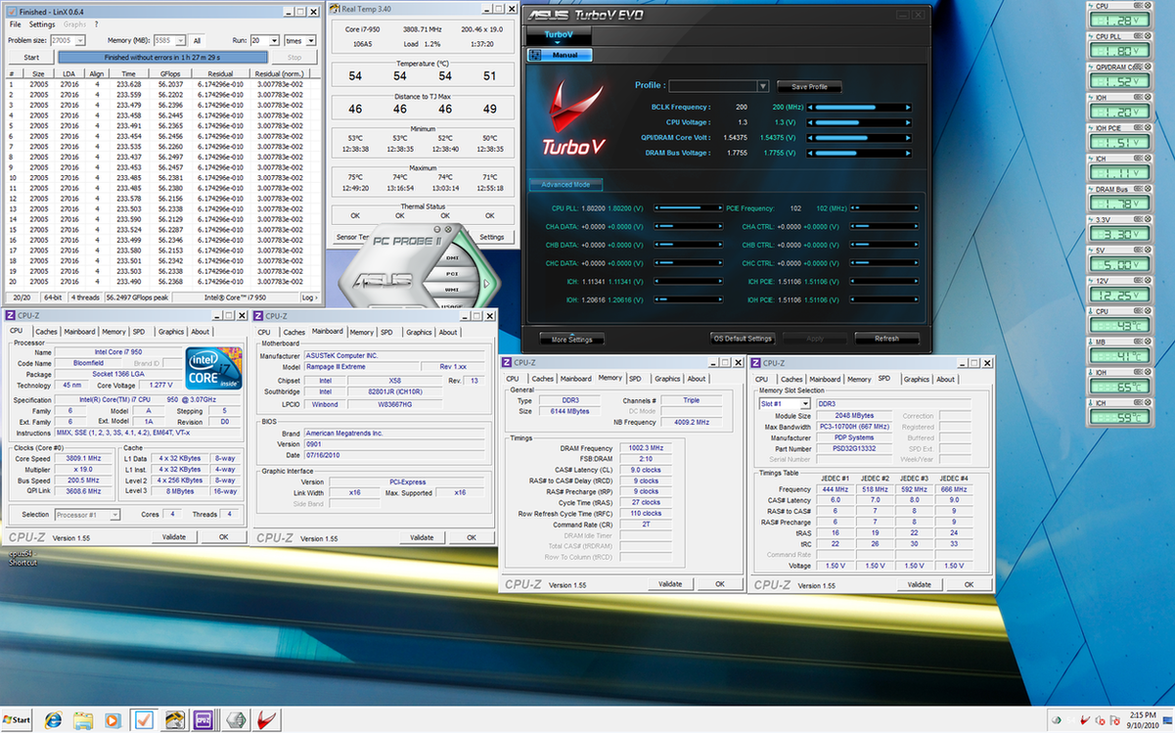
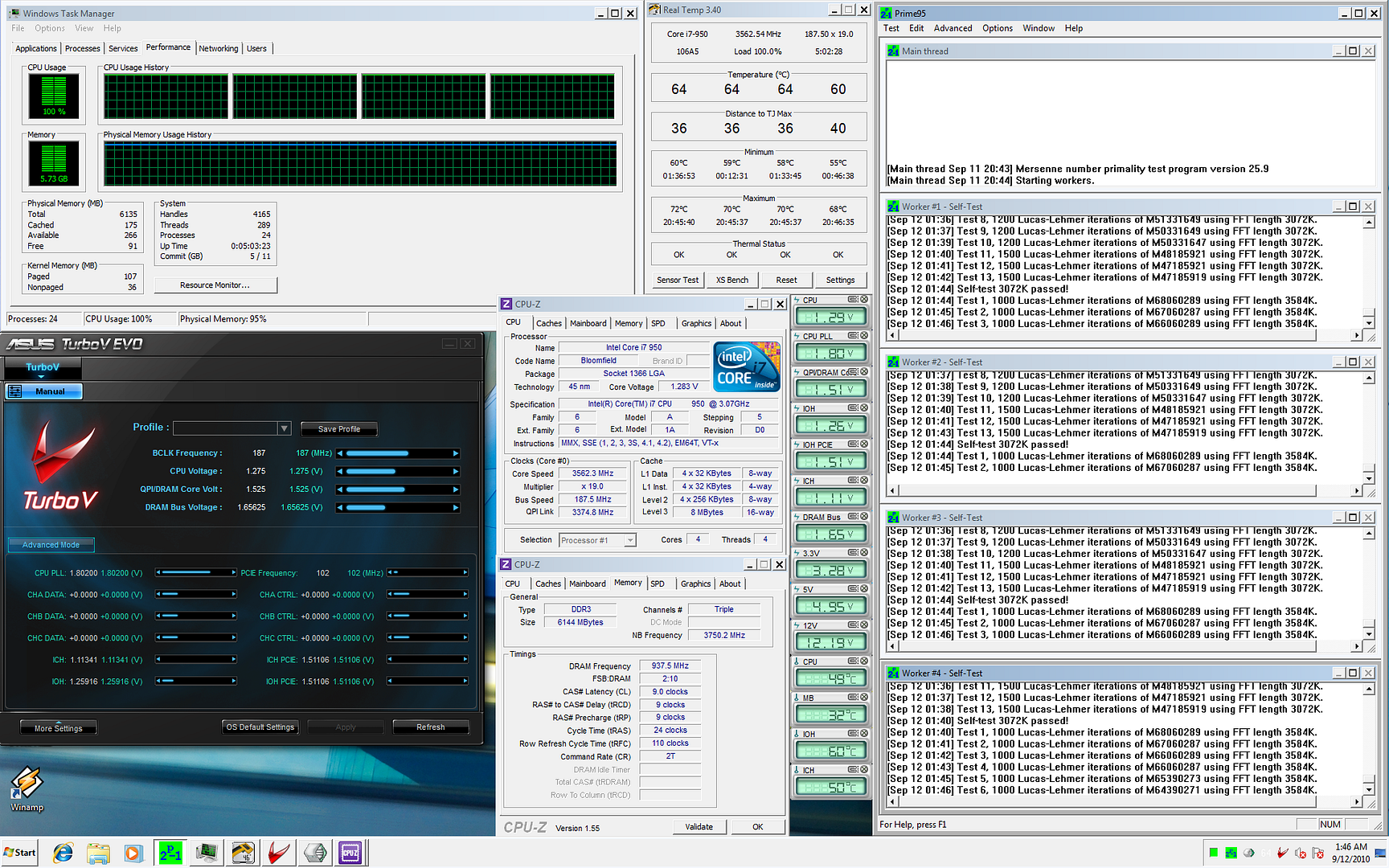
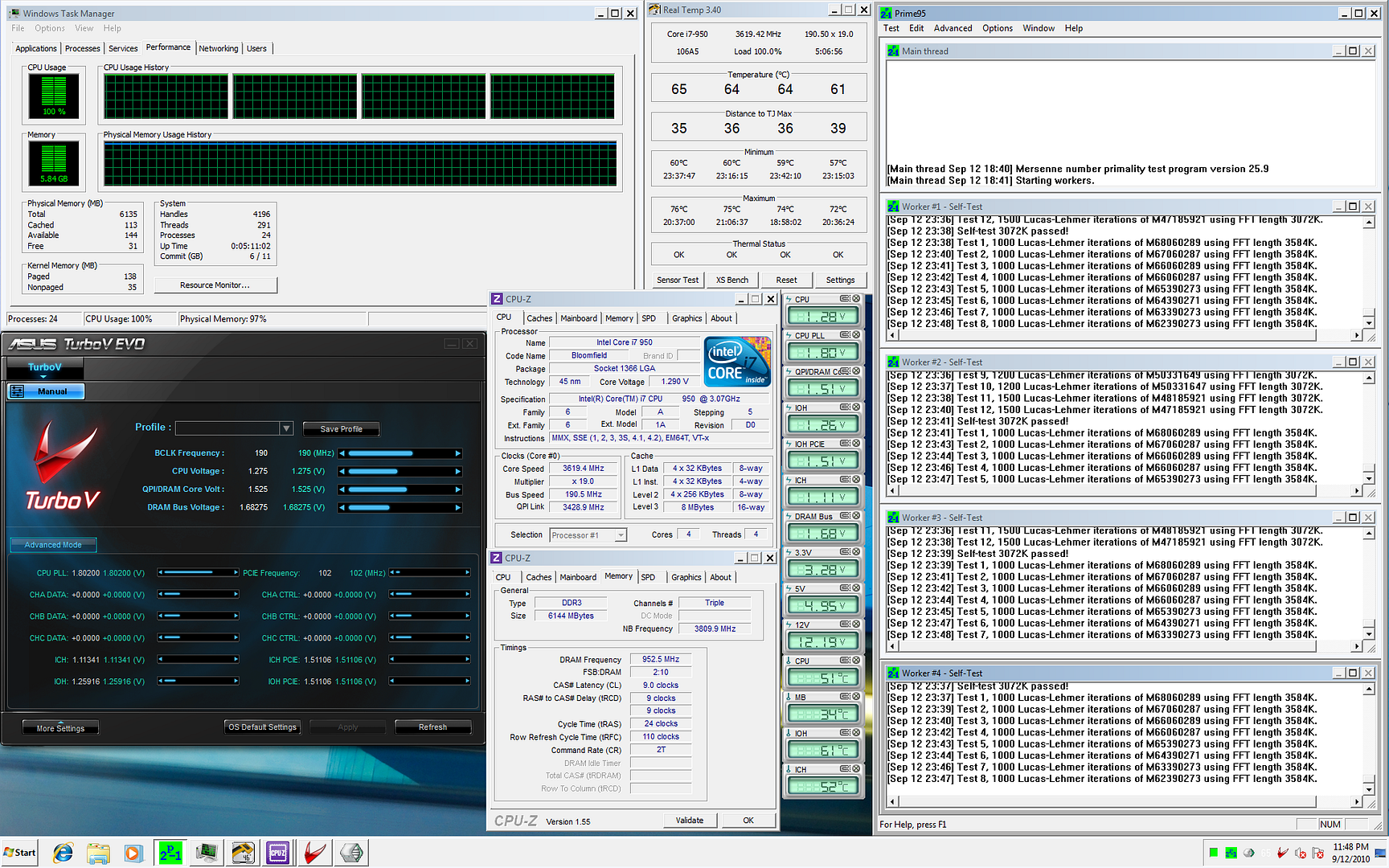

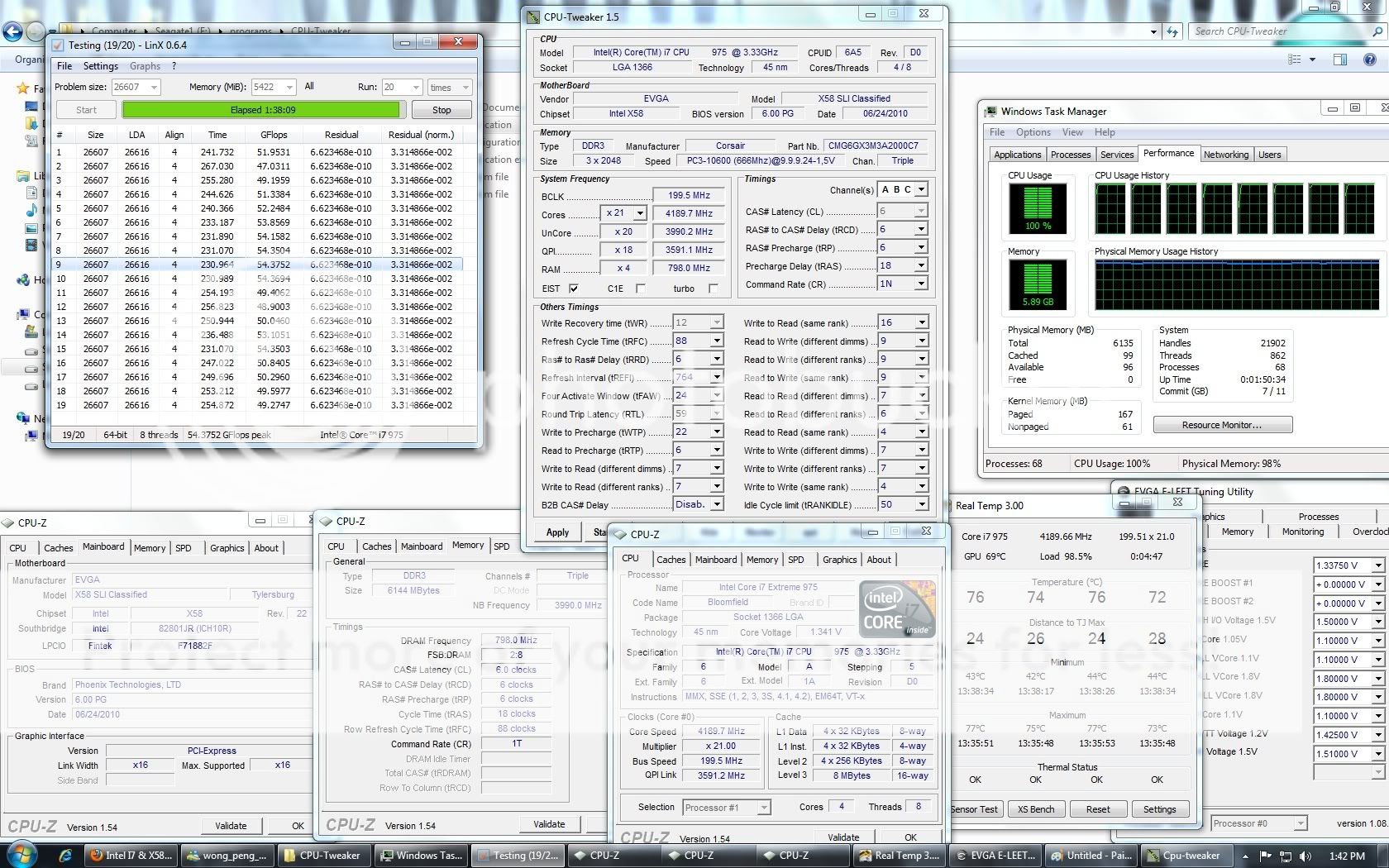
 0.0291sec
0.0291sec
 0.22
0.22
 6 queries
6 queries
 GZIP Disabled
GZIP Disabled