
This is Ivy Bridge (IB) overclocking thread.
Please share your benchmark, stability, guides etc...
Latest BIOS:
LINK
Latest Overclocking Programs, System Info, Benchmarking, & Stability Tools
LINK - credit to stasio
Monitoring Tools:
CPU-Z 1.67
RealTemp 3.70
ReadlTemp TI
CoreTemp 1.0 RC5
HWiNFO 4.22
Mem TweakIT 2.00.01
CPU-Tweaker 2.0 Beta 15
GIGABYTE Tweak Launcher
Z87 OC Button
ASRock OC Tools 0724
ASUS TurboVCore
Stability/Stressing Tools: - Please use Win7 Service Pack 1 (SP1), take a screenshot before the test finished.
LinX 0.6.4 (10.3.7) - set memory to "ALL" preset
LinX 0.6.5 (11.1.0.002)
Prime95 28.1 Build 2 X64
Linpack 11.0.5.009
OCCT 4.4.0
» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
Benchmark Tools:
SuperPI Mod XS 1.5
HyperPI 0.99 Beta
AIDA64 3.00.2590
Cinebench 11.5
wprime 2.09
pifast
maxxmem
AquaMark 3.1
OC Tips & Guides
AnandTech - Undervolting & Overclocking on Ivy Bridge
shamino's Mem OC Guide on M5G
Z77 UEFI OC Tuning Guide
Gigabyte Ivy Bridge/Z77 Overclocking Guide
ASUS Maximus V Formula OC Guide
Sandy / Ivy Bridge | Complete Overclocking Guide | *ASRock Edition*
owikh84's BIOS settings for 5GHz
Memory Overclocking Guide for Intel Ivy Bridge platform
QUOTE(owikh84 @ May 12 2012, 09:36 AM)
All offset voltage does is change the voltage under load. So, if your stock voltage is 1.30v and you offset it +0.05v, you will get 1.35v under load. It allows your computer to idle at a very low voltage. Basically the offset is how much voltage you want to add to your CPU under load.
Manual = voltage is always that unless affected by load line calibration LLC.
Offset = whatever the Intel set VID voltage is + your offset
So if your VID for 1.6GHz is 0.900v, with +0.050 offset you will make it 0.950v
VID at 2.5GHz is 0.950v, you will make it 1.000v
VID at 3.2GHz is 1.050v, you will make it 1.100v
VID at 3.7GHz is 1.100v, you will make it 1.15v
etc....
You might wanna go through this guide completely written for offset clockings:
Overclocking Using Offset Mode for CPU Core Voltage
Manual = voltage is always that unless affected by load line calibration LLC.
Offset = whatever the Intel set VID voltage is + your offset
So if your VID for 1.6GHz is 0.900v, with +0.050 offset you will make it 0.950v
VID at 2.5GHz is 0.950v, you will make it 1.000v
VID at 3.2GHz is 1.050v, you will make it 1.100v
VID at 3.7GHz is 1.100v, you will make it 1.15v
etc....
You might wanna go through this guide completely written for offset clockings:
Overclocking Using Offset Mode for CPU Core Voltage
===========================================================================
Latest News & Updates:
Removing the absolute CRAP thermal packaging on the ivy bridge cpu AKA IHS - credit to kelvin_hata
i7-3770k tested with IHS removed. Results?
Delidded Ivy Bridge Club
===========================================================================
3770K & 3570K Reviews:
» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
=============================================================================
Z77 Motherboards Reviews:
» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
=============================================================================
DRAM Reviews:
» Click to show Spoiler - click again to hide... «
Corsair RAM IC:

G.Skill RAM IC:
QUOTE(stasio @ Aug 30 2012, 12:11 AM)
0000 = Hynix
AB40 = samsung
0140 = Micron
0240 = Hynix
0340 = samsung
0360 = Samsung
0640 = Elpida non-Hyper
0650 = Elpida (seen on blue PCB Tridents)
0660 = Elpida non-Hyper
0690 = Elpida Hyper
1040 = PSC
1240 = Nanya (?)
1400 = Hynix
1500 = Samsung
1600 = Hynix
2400 = Hynix
AB40 = samsung
0140 = Micron
0240 = Hynix
0340 = samsung
0360 = Samsung
0640 = Elpida non-Hyper
0650 = Elpida (seen on blue PCB Tridents)
0660 = Elpida non-Hyper
0690 = Elpida Hyper
1040 = PSC
1240 = Nanya (?)
1400 = Hynix
1500 = Samsung
1600 = Hynix
2400 = Hynix
=============================================================================
BSOD codes for overclocking
QUOTE
0x101 = increase vcore
0x124 = increase/decrease vcore or QPI/VTT... have to test to see which one it is
0x0A = unstable RAM/IMC, increase QPI first, if that doesn't work increase vcore
0x1E = increase vcore
0x3B = increase vcore
0x3D = increase vcore
0xD1 = QPI/VTT, increase/decrease as necessary, can also be unstable Ram, raise Ram voltage
0x9C = QPI/VTT most likely, but increasing vcore has helped in some instances
0x50 = RAM timings/Frequency or uncore multi unstable, increase RAM voltage or adjust QPI/VTT, or lower uncore if you're higher than 2x
0x109 = Not enough or too Much memory voltage
0x116 = Low IOH (NB) voltage, GPU issue (most common when running multi-GPU/overclocking GPU)
0x7E = Corrupted OS file, possibly from overclocking. Run sfc /scannow and chkdsk /r
0x124 = increase/decrease vcore or QPI/VTT... have to test to see which one it is
0x0A = unstable RAM/IMC, increase QPI first, if that doesn't work increase vcore
0x1E = increase vcore
0x3B = increase vcore
0x3D = increase vcore
0xD1 = QPI/VTT, increase/decrease as necessary, can also be unstable Ram, raise Ram voltage
0x9C = QPI/VTT most likely, but increasing vcore has helped in some instances
0x50 = RAM timings/Frequency or uncore multi unstable, increase RAM voltage or adjust QPI/VTT, or lower uncore if you're higher than 2x
0x109 = Not enough or too Much memory voltage
0x116 = Low IOH (NB) voltage, GPU issue (most common when running multi-GPU/overclocking GPU)
0x7E = Corrupted OS file, possibly from overclocking. Run sfc /scannow and chkdsk /r

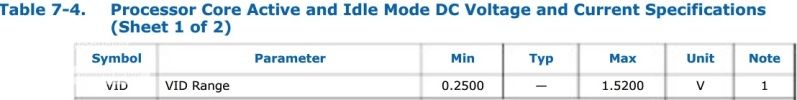
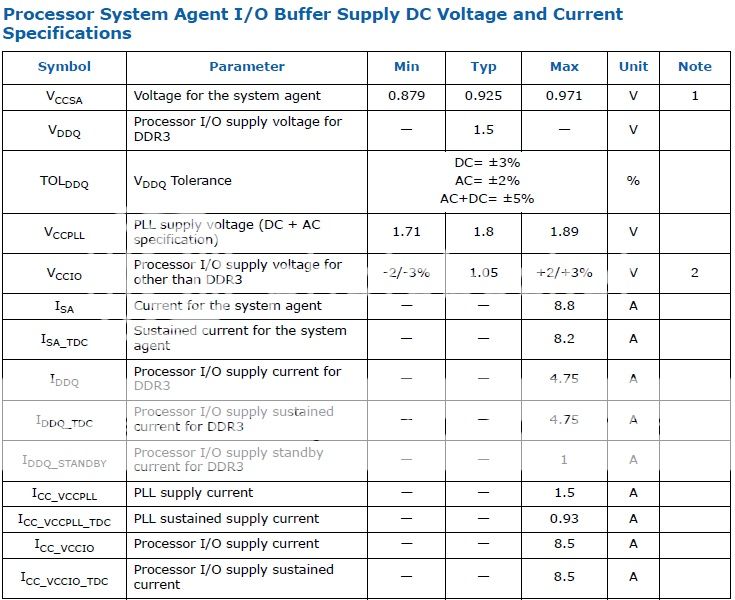
Source
This post has been edited by owikh84: Oct 15 2013, 09:00 PM


 Apr 20 2012, 12:32 AM, updated 10y ago
Apr 20 2012, 12:32 AM, updated 10y ago
 Quote
Quote











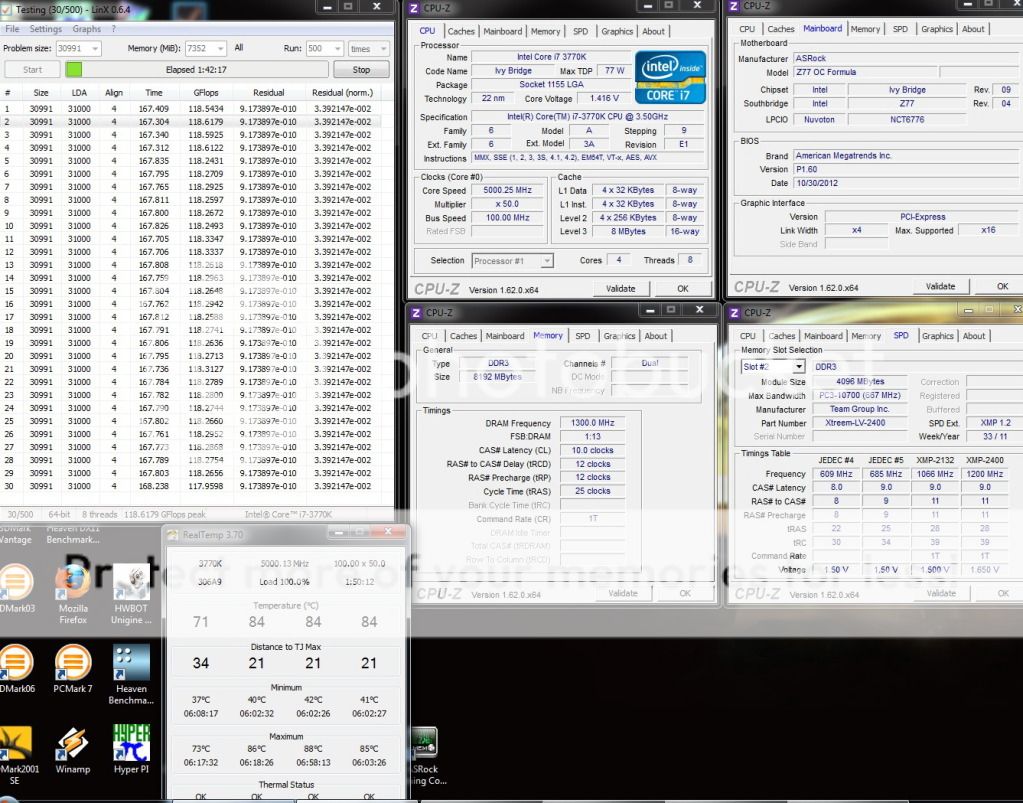





















 0.0195sec
0.0195sec
 0.61
0.61
 6 queries
6 queries
 GZIP Disabled
GZIP Disabled